295 lines
7.5 KiB
Markdown
295 lines
7.5 KiB
Markdown
<h2><center>Nginx匹配</center></h2>
|
||
|
||
------
|
||
|
||
## 一:Location匹配
|
||
|
||
### 1. location简介
|
||
|
||
location 指令是 nginx 中最关键的指令之一,location 指令的功能是用来匹配不同的 URI 请求,进而对请求做不同的处理和响应。
|
||
|
||
### 2. location语法
|
||
|
||
```nginx
|
||
Nginx 的 HTTP 配置主要包括三个区块,结构如下:
|
||
|
||
http { # 这个是协议级别
|
||
include mime.types;
|
||
default_type application/octet-stream;
|
||
keepalive_timeout 65;
|
||
gzip on;
|
||
server { # 这个是服务器级别
|
||
listen 80;
|
||
server_name localhost;
|
||
|
||
location / { # 这个是请求级别
|
||
root html;
|
||
index index.html index.htm;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
location ~ \.(html|jpg)$ {
|
||
root /web;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
浏览器-->地址栏-->URI -->http:// --> 主机:80 -->http协议块的配置 --> server --> location -->页面内容-->返回客户端浏览器
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
```nginx
|
||
location 区段
|
||
|
||
- location 是在 server 块中配置,根据不同的 URI 使用不同的配置,来处理不同的请求。
|
||
|
||
- location 是有顺序的,会根据不同请求配置的优先级来匹配的location 处理。
|
||
|
||
基本语法如下:
|
||
location [=|~|~*|^~|@] pattern{……}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
### 3. location前缀含义
|
||
|
||
```nginx
|
||
= 表示精确匹配,优先级也是最高的
|
||
|
||
^~ 表示uri以某个常规字符串开头,理解为匹配url路径即可
|
||
~ 表示区分大小写的正则匹配
|
||
~* 表示不区分大小写的正则匹配
|
||
|
||
!~ 表示区分大小写不匹配的正则
|
||
!~* 表示不区分大小写不匹配的正则
|
||
/ 通用匹配,任何请求都会匹配到
|
||
|
||
@ 内部服务跳转
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
### 4. 查找顺序和优先级
|
||
|
||
```nginx
|
||
= 大于 ^~ 大于 ~|~* 大于 !~|!~* 大于 /
|
||
多个location配置的情况下匹配顺序为:首先匹配 =,其次匹配^~, 其次是按正则匹配,最后是交给 / 通用匹配。当有匹配成功时候,停止匹配,按当前匹配规则处理请求。
|
||
|
||
Named Location (location @): 使用@符号定义的命名位置块不匹配URI前缀,而是根据具体的用途或配置定义来执行内部重定向。它们通常不与请求URI的前缀直接匹配,因此不涉及前缀匹配的优先级。
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
### 5. 配置实例
|
||
|
||
1. 没有修饰符 表示:必须以指定模式开始
|
||
|
||
```bash
|
||
[root@test ~]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/test.conf
|
||
server {
|
||
listen 80;
|
||
server_name 192.168.159.130;
|
||
location / {
|
||
root /usr/share/nginx/web;
|
||
index index.html index.htm;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
location /abc {
|
||
alias /usr/share/nginx/web/a.html;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
测试:
|
||
[root@test ~]# curl http://192.168.159.130
|
||
web1
|
||
[root@test ~]# curl http://192.168.159.130/abc
|
||
web2
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
2. =表示:必须与指定的模式精确匹配
|
||
|
||
```bash
|
||
[root@test ~]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/test.conf
|
||
server {
|
||
listen 80;
|
||
server_name 192.168.159.130;
|
||
location / {
|
||
root /usr/share/nginx/web;
|
||
index index.html index.htm;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
location = / {
|
||
root /usr/share/nginx/web;
|
||
index index.html index.htm;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
测试:
|
||
[root@test ~]# curl http://192.168.159.130/
|
||
/
|
||
[root@test ~]# curl http://192.168.159.130/a.html
|
||
= /
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
3. ~ 表示:指定的正则表达式要区分大小写
|
||
|
||
```bash
|
||
[root@test ~]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/test.conf
|
||
server {
|
||
listen 80;
|
||
server_name 192.168.159.130;
|
||
location ~ \.(html|jpg|png|js|css|gif|bmp|jpeg)$ {
|
||
root /usr/share/nginx/web;
|
||
index index.html index.htm;
|
||
expires 1d; #为客户端设置静态资源缓存时间
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
测试:
|
||
[root@test ~]# curl 192.168.159.130:80/index.html
|
||
web1
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
4. ~* 表示:指定的正则表达式不区分大小写
|
||
|
||
```bash
|
||
[root@test ~]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/test.conf
|
||
server {
|
||
listen 80;
|
||
server_name 192.168.159.130;
|
||
location ~* \.(HTML|css)$ {
|
||
root /usr/share/nginx/web;
|
||
index index.html index.htm;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
[root@test ~]# curl http://192.168.159.130/a.html
|
||
= /
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
5. ^~ :类似于无修饰符的行为,也是以指定模式开始,不同的是,如果模式匹配,那么就停止搜索其他模式了
|
||
|
||
```bash
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
### 6. 案例
|
||
|
||

|
||
|
||
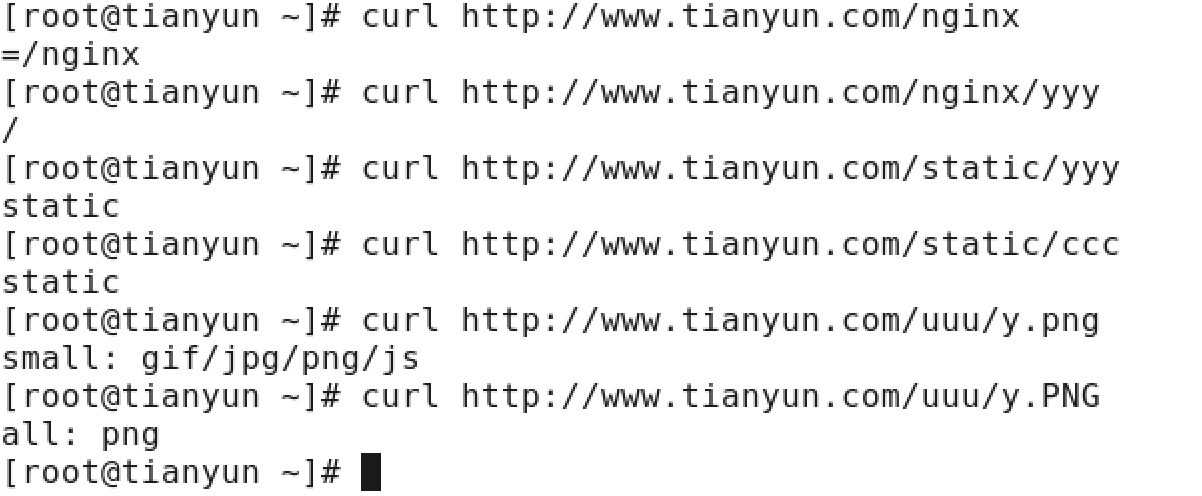
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
### 7. echo模块
|
||
|
||
获取nginx的安装版本:
|
||
|
||
```bash
|
||
[root@test ~]# nginx -v
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
下载一个相同版本的nginx包,并解压
|
||
|
||
```bash
|
||
[root@test ~]# wget https://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.16.0.tar.gz
|
||
[root@test ~]# tar xzf nginx-1.16.0.tar.gz -C /usr/local/
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
下载echo模块的安装包,并解压到指定位置
|
||
|
||
```bash
|
||
[root@test ~]# wget https://github.com/openresty/echo-nginx-module/archive/v0.61.tar.gz
|
||
[root@test ~]# tar xzf v0.61.tar.gz -C /usr/local/
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
安装编译所需软件:
|
||
|
||
```bash
|
||
[root@test ~]# yum install -y pcre* openssl* gcc gcc-c++ make
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
获取源nginx的配置:
|
||
|
||
```bash
|
||
[root@test ~]# nginx -V
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
添加上原来已经有的参数和新添加的模块:
|
||
|
||
```bash
|
||
[root@test ~]# ./configure --prefix=/etc/nginx --sbin-path=/usr/sbin/nginx --modules-path=/usr/lib64/nginx/modules --conf-path=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf --error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/error.log --http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log --pid-path=/var/run/nginx.pid --lock-path=/var/run/nginx.lock --http-client-body-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/client_temp --http-proxy-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/proxy_temp --http-fastcgi-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/fastcgi_temp --http-uwsgi-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/uwsgi_temp --http-scgi-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/scgi_temp --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-compat --with-file-aio --with-threads --with-http_addition_module --with-http_auth_request_module --with-http_dav_module --with-http_flv_module --with-http_gunzip_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-http_mp4_module --with-http_random_index_module --with-http_realip_module --with-http_secure_link_module --with-http_slice_module --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_sub_module --with-http_v2_module --with-mail --with-mail_ssl_module --with-stream --with-stream_realip_module --with-stream_ssl_module --with-stream_ssl_preread_module --add-module=/usr/local/echo-nginx-module-0.61
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
重新编译:
|
||
|
||
```bash
|
||
[root@test ~]# make
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
将原来的nignx备份:
|
||
|
||
```bash
|
||
[root@test ~]# mv /usr/sbin/nginx /usr/sbin/nginx_bak
|
||
[root@test ~]# cp objs/nginx /usr/sbin/
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
重新启动:
|
||
|
||
```bash
|
||
[root@test ~]# systemctl restart nginx
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
使用echo:
|
||
|
||
```bash
|
||
配置 $foo=hello
|
||
[root@test ~]# cd /etc/nginx/conf.d/
|
||
[root@test conf.d]# vim echo.conf
|
||
server {
|
||
listen 80;
|
||
server_name localhost;
|
||
location /test {
|
||
set $foo hello;
|
||
echo "foo: $foo";
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
[root@test conf.d]# nginx -s reload
|
||
[root@test conf.d]# curl localhost/test
|
||
foo: hello
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
### 8. alias和root
|
||
|
||
- alias 是一个目录别名的定义
|
||
- root 则是最上层目录的定义
|
||
|
||
还有一个重要的区别是alias后面必须要用“/”结束,否则会找不到文件的,而root则可有可无。
|
||
|
||
```shell
|
||
location /img/ {
|
||
alias /var/www/image/;
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
若按照上述配置的话,则访问/img/目录里面的文件时,ningx会自动去/var/www/image/目录找文件。
|
||
|
||
```shell
|
||
location /img/ {
|
||
root /var/www/image;
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
若按照这种配置的话,则访问/img/目录下的文件时,nginx会去/var/www/image/img/目录下找文件。
|