diff --git a/Elasticsearch.md b/Elasticsearch.md
index 493b0ad..cae8e73 100644
--- a/Elasticsearch.md
+++ b/Elasticsearch.md
@@ -1,1101 +1,1101 @@
-Elasticsearch 集群搭建
-
-------
-
-## 一:环境准备
-
-### 1. 简介
-
- 部署模式:es集群采用无主模式
-
- es版本:8.13.4
-
- jdk版本:使用es内嵌的jdk21,无需额外安装jdk环境
-
- 操作系统:Centos 7
-
-### 2. 环境
-
-| IP地址 | 主机名 | 角色 |
-| :-------------: | :-------------: | :-------------: |
-| 192.168.159.131 | elasticsearch01 | master&data节点 |
-| 192.168.159.132 | elasticsearch02 | master&data节点 |
-| 192.168.159.133 | elasticsearch03 | master&data节点 |
-
-## 二:服务器配置
-
-### 1. 创建用户
-
-es不能使用root用户进行部署,故创建新用户管理es集群
-
-```bash
-# 添加一个用户 elasticsearch 密码 elasticsearch
-[root@elasticsearch1 ~]# useradd elasticsearch && echo elasticsearch | passwd --stdin elasticsearch
-```
-
-### 2. 本地解析
-
-```bash
-[root@elasticsearch1 ~]# vim /etc/hosts
-192.168.159.131 elasticsearch1
-192.168.159.132 elasticsearch2
-192.168.159.133 elasticsearch3
-```
-
-### 3. 系统优化
-
-优化最大进程数,最大文件打开数,优化虚拟内存
-
-```bash
-[root@elasticsearch1 ~]# vim /etc/security/limits.conf
-* soft nofile 65536
-* hard nofile 131072
-* soft nproc 4096
-* hard nproc 6553
-
-[root@elasticsearch1 ~]# vim /etc/sysctl.conf
-vm.max_map_count=262144
-
-[root@elasticsearch1 ~]# sysctl -p
-vm.max_map_count = 262144
-```
-
-## 三:集群部署
-
-### 1. 获取安装包
-
-官网:[Past Releases of Elastic Stack Software | Elastic](https://www.elastic.co/downloads/past-releases#elasticsearch)
-
-```bash
-[root@elasticsearch1 ~]# wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-8.13.4-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
-```
-
-### 2. 解压安装
-
-```bash
-[root@elasticsearch1 ~]# tar xf elasticsearch-8.13.4-linux-x86_64.tar.gz -C /usr/local/
-[root@elasticsearch1 ~]# mv /usr/local/elasticsearch-8.13.4/ /usr/local/elasticsearch
-[root@elasticsearch1 ~]# chown -R elasticsearch:elasticsearch /usr/local/elasticsearch
-```
-
-### 3. 配置环境变量
-
-```bash
-[root@elasticsearch1 ~]# vim /etc/profile
-JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/elasticsearch/jdk
-ES_HOME=/usr/local/elasticsearch
-PATH=$PATH:$JAVA_HOME/bin:$ES_HOME/bin
-export JAVA_HOME ES_HOME PATH
-
-# 刷新环境变量
-[root@elasticsearch1 ~]# source /etc/profile
-
-[root@elasticsearch1 ~]# java -version
-openjdk version "21.0.2" 2024-01-16
-OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 21.0.2+13-58)
-OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 21.0.2+13-58, mixed mode, sharing)
-```
-
-### 4. 创建目录
-
-目录用来存储数据和存放证书并赋予权限
-
-```bash
-[root@elasticsearch1 ~]# mkdir -p /usr/local/elasticsearch/data
-[root@elasticsearch1 ~]# mkdir -p /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs
-[root@elasticsearch1 ~]# chown -R elasticsearch:elasticsearch /usr/local/elasticsearch/
-```
-
-**注意:截至到目前为止,所有节点服务器的操作都是一致的**
-
-### 5. 签发证书
-
-```bash
-# 在第一台服务器节点 elasticsearch1 设置集群多节点通信密钥
-# 切换用户
-[root@elasticsearch1 ~]# su - elasticsearch
-[elasticsearch@elasticsearch1 ~]$ cd /usr/local/elasticsearch/bin/
-[elasticsearch@elasticsearch1 bin]$ ./elasticsearch-certutil ca
-warning: ignoring JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/elasticsearch/jdk; using bundled JDK
-This tool assists you in the generation of X.509 certificates and certificate
-signing requests for use with SSL/TLS in the Elastic stack.
-
-The 'ca' mode generates a new 'certificate authority'
-This will create a new X.509 certificate and private key that can be used
-to sign certificate when running in 'cert' mode.
-
-Use the 'ca-dn' option if you wish to configure the 'distinguished name'
-of the certificate authority
-
-By default the 'ca' mode produces a single PKCS#12 output file which holds:
- * The CA certificate
- * The CA's private key
-
-If you elect to generate PEM format certificates (the -pem option), then the output will
-be a zip file containing individual files for the CA certificate and private key
-
-Please enter the desired output file [elastic-stack-ca.p12]:
-Enter password for elastic-stack-ca.p12 :
-
-# 用 ca 证书签发节点证书,过程中需按三次回车键,生成目录:elasticsearch的home:/usr/local/elasticsearch/
-[elasticsearch@elasticsearch1 bin]$ ./elasticsearch-certutil cert --ca elastic-stack-ca.p12
-...
-If you specify any of the following options:
- * -pem (PEM formatted output)
- * -multiple (generate multiple certificates)
- * -in (generate certificates from an input file)
-then the output will be be a zip file containing individual certificate/key files
-
-Enter password for CA (elastic-stack-ca.p12) :
-Please enter the desired output file [elastic-certificates.p12]:
-Enter password for elastic-certificates.p12 :
-
-Certificates written to /usr/local/elasticsearch/elastic-certificates.p12
-
-This file should be properly secured as it contains the private key for
-your instance.
-This file is a self contained file and can be copied and used 'as is'
-For each Elastic product that you wish to configure, you should copy
-this '.p12' file to the relevant configuration directory
-and then follow the SSL configuration instructions in the product guide.
-
-For client applications, you may only need to copy the CA certificate and
-configure the client to trust this certificate.
-
-# 将生成的证书文件移动到 config/certs 目录中
-[elasticsearch@elasticsearch1 bin]$ cd /usr/local/elasticsearch/
-[elasticsearch@elasticsearch1 elasticsearch]$ ls -l | grep "elastic-"
--rw------- 1 elasticsearch elasticsearch 3596 4月 29 19:21 elastic-certificates.p12
--rw------- 1 elasticsearch elasticsearch 2672 4月 29 19:19 elastic-stack-ca.p12
-[elasticsearch@elasticsearch1 elasticsearch]$ mv elastic-certificates.p12 config/certs/
-[elasticsearch@elasticsearch1 elasticsearch]$ mv elastic-stack-ca.p12 config/certs/
-```
-
-### 6. 设置集群多节点HTTP证书
-
-```bash
-[elasticsearch@elasticsearch1 elasticsearch]$ cd /usr/local/elasticsearch/bin/
-[elasticsearch@elasticsearch1 bin]$ ./elasticsearch-certutil http
-warning: ignoring JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/elasticsearch/jdk; using bundled JDK
-
-## Elasticsearch HTTP Certificate Utility
-
-The 'http' command guides you through the process of generating certificates
-for use on the HTTP (Rest) interface for Elasticsearch.
-
-This tool will ask you a number of questions in order to generate the right
-set of files for your needs.
-
-## Do you wish to generate a Certificate Signing Request (CSR)?
-
-A CSR is used when you want your certificate to be created by an existing
-Certificate Authority (CA) that you do not control (that is, you don't have
-access to the keys for that CA).
-
-If you are in a corporate environment with a central security team, then you
-may have an existing Corporate CA that can generate your certificate for you.
-Infrastructure within your organisation may already be configured to trust this
-CA, so it may be easier for clients to connect to Elasticsearch if you use a
-CSR and send that request to the team that controls your CA.
-
-If you choose not to generate a CSR, this tool will generate a new certificate
-for you. That certificate will be signed by a CA under your control. This is a
-quick and easy way to secure your cluster with TLS, but you will need to
-configure all your clients to trust that custom CA.
-######################################################
-# 是否生成CSR,选择 N ,不需要 #
-######################################################
-Generate a CSR? [y/N]N
-
-## Do you have an existing Certificate Authority (CA) key-pair that you wish to use to sign your certificate?
-
-If you have an existing CA certificate and key, then you can use that CA to
-sign your new http certificate. This allows you to use the same CA across
-multiple Elasticsearch clusters which can make it easier to configure clients,
-and may be easier for you to manage.
-
-If you do not have an existing CA, one will be generated for you.
-########################################################
-# 是否使用已经存在的CA证书,选择 y ,因为已经创建签发好了CA #
-########################################################
-Use an existing CA? [y/N]y
-
-## What is the path to your CA?
-
-Please enter the full pathname to the Certificate Authority that you wish to
-use for signing your new http certificate. This can be in PKCS#12 (.p12), JKS
-(.jks) or PEM (.crt, .key, .pem) format.
-######################################################
-# 指定CA证书的路径地址,CA Path:后写绝对路径 #
-######################################################
-CA Path: /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs/elastic-stack-ca.p12
-Reading a PKCS12 keystore requires a password.
-It is possible for the keystore's password to be blank,
-in which case you can simply press at the prompt
-######################################################
-# 设置密钥库的密码,直接 回车 即可 #
-######################################################
-Password for elastic-stack-ca.p12:
-
-## How long should your certificates be valid?
-
-Every certificate has an expiry date. When the expiry date is reached clients
-will stop trusting your certificate and TLS connections will fail.
-
-Best practice suggests that you should either:
-(a) set this to a short duration (90 - 120 days) and have automatic processes
-to generate a new certificate before the old one expires, or
-(b) set it to a longer duration (3 - 5 years) and then perform a manual update
-a few months before it expires.
-
-You may enter the validity period in years (e.g. 3Y), months (e.g. 18M), or days (e.g. 90D)
-######################################################
-# 设置证书的失效时间,这里的y表示年,5y则代表失效时间5年 #
-######################################################
-For how long should your certificate be valid? [5y] 5y
-
-## Do you wish to generate one certificate per node?
-
-If you have multiple nodes in your cluster, then you may choose to generate a
-separate certificate for each of these nodes. Each certificate will have its
-own private key, and will be issued for a specific hostname or IP address.
-
-Alternatively, you may wish to generate a single certificate that is valid
-across all the hostnames or addresses in your cluster.
-
-If all of your nodes will be accessed through a single domain
-(e.g. node01.es.example.com, node02.es.example.com, etc) then you may find it
-simpler to generate one certificate with a wildcard hostname (*.es.example.com)
-and use that across all of your nodes.
-
-However, if you do not have a common domain name, and you expect to add
-additional nodes to your cluster in the future, then you should generate a
-certificate per node so that you can more easily generate new certificates when
-you provision new nodes.
-#########################################################
-# 是否需要为每个节点都生成证书,选择 N 无需每个节点都配置证书#
-#########################################################
-Generate a certificate per node? [y/N]N
-
-## Which hostnames will be used to connect to your nodes?
-
-These hostnames will be added as "DNS" names in the "Subject Alternative Name"
-(SAN) field in your certificate.
-
-You should list every hostname and variant that people will use to connect to
-your cluster over http.
-Do not list IP addresses here, you will be asked to enter them later.
-
-If you wish to use a wildcard certificate (for example *.es.example.com) you
-can enter that here.
-
-Enter all the hostnames that you need, one per line.
-############################################################
-# 输入需连接集群节点主机名信息,一行输入一个IP地址,空行回车结束 #
-############################################################
-When you are done, press once more to move on to the next step.
-
-elasticsearch1
-elasticsearch2
-elasticsearch3
-
-You entered the following hostnames.
-
- - elasticsearch1
- - elasticsearch2
- - elasticsearch3
-
-####################################################
-# 确认以上是否为正确的配置,输入 Y 表示信息正确 #
-####################################################
-Is this correct [Y/n]Y
-
-## Which IP addresses will be used to connect to your nodes?
-
-If your clients will ever connect to your nodes by numeric IP address, then you
-can list these as valid IP "Subject Alternative Name" (SAN) fields in your
-certificate.
-
-If you do not have fixed IP addresses, or not wish to support direct IP access
-to your cluster then you can just press to skip this step.
-
-Enter all the IP addresses that you need, one per line.
-#########################################################
-# 输入需连接集群节点IP信息,一行输入一个IP地址,空行回车结束 #
-#########################################################
-When you are done, press once more to move on to the next step.
-
-192.168.159.131
-192.168.159.132
-192.168.159.133
-
-You entered the following IP addresses.
-
- - 192.168.159.131
- - 192.168.159.132
- - 192.168.159.133
-
-####################################################
-# 确认以上是否为正确的配置,输入 Y 表示信息正确 #
-####################################################
-Is this correct [Y/n]Y
-
-## Other certificate options
-
-The generated certificate will have the following additional configuration
-values. These values have been selected based on a combination of the
-information you have provided above and secure defaults. You should not need to
-change these values unless you have specific requirements.
-
-Key Name: elasticsearch1
-Subject DN: CN=elasticsearch1
-Key Size: 2048
-####################################################
-# 是否要更改以上这些选项,选择 N ,不更改证书选项配置 #
-####################################################
-Do you wish to change any of these options? [y/N]N
-
-## What password do you want for your private key(s)?
-
-Your private key(s) will be stored in a PKCS#12 keystore file named "http.p12".
-This type of keystore is always password protected, but it is possible to use a
-blank password.
-####################################################
-# 是否要给证书加密,不需要加密,两次 回车 即可 #
-####################################################
-If you wish to use a blank password, simply press at the prompt below.
-Provide a password for the "http.p12" file: [ for none]
-
-## Where should we save the generated files?
-
-A number of files will be generated including your private key(s),
-public certificate(s), and sample configuration options for Elastic Stack products.
-
-These files will be included in a single zip archive.
-
-What filename should be used for the output zip file? [/usr/local/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-ssl-http.zip]
-
-Zip file written to /usr/local/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-ssl-http.zip
-```
-
-### 7. 分发证书
-
-```bash
-# 解压
-[elasticsearch@elasticsearch1 bin]$ cd /usr/local/elasticsearch/
-[elasticsearch@elasticsearch1 elasticsearch]$ unzip elasticsearch-ssl-http.zip
-
-# 移动证书
-[elasticsearch@elasticsearch1 elasticsearch]$ mv ./elasticsearch/http.p12 config/certs/
-[elasticsearch@elasticsearch1 elasticsearch]$ mv ./kibana/elasticsearch-ca.pem config/certs/
-
-# 将证书分发到其他节点02 03
-[elasticsearch@elasticsearch1 elasticsearch]$ exit
-登出
-[root@elasticsearch1 ~]# cd /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs/
-[root@elasticsearch1 certs]# scp ./* elasticsearch2:/usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs/
-[root@elasticsearch1 certs]# scp ./* elasticsearch3:/usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs/
-
-# 修改属主属组
-[root@elasticsearch2/3 ~]#chown -R /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs/*
-```
-
-### 8. 修改配置
-
-```bash
-[root@elasticsearch1/2/3 certs]# cd /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/
-[root@elasticsearch1/2/3 config]# vim elasticsearch.yml
-cluster.name: elasticsearch
-node.name: elasticsearch1
-path.data: /usr/local/elasticsearch/data
-path.logs: /usr/local/elasticsearch/logs
-network.host: 0.0.0.0
-http.port: 9200
-discovery.seed_hosts: ["192.168.159.131:9200", "192.168.159.132:9200","192.168.159.133:9200"]
-cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["elasticsearch1", "elasticsearch2","elasticsearch3"]
-xpack.security.enabled: true
-xpack.security.enrollment.enabled: true
-xpack.security.http.ssl:
- enabled: true
- keystore.path: /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs/http.p12
- keystore.password: 123456 # 如果生成证书时设置了密码则要添加密码配置
- truststore.path: /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs/http.p12
- truststore.password: 123456 # 如果生成证书时设置了密码则要添加密码配置
-xpack.security.transport.ssl:
- enabled: true
- verification_mode: certificate
- keystore.path: /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs/elastic-certificates.p12
- keystore.password: 123456 # 如果生成证书时设置了密码则要添加密码配置
- truststore.path: /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs/elastic-certificates.p12
- truststore.password: 123456 # 如果生成证书时设置了密码则要添加密码配置
-http.host: [_local_, _site_]
-ingest.geoip.downloader.enabled: false
-xpack.security.http.ssl.client_authentication: none
-```
-
-注意:
-
-- xpack.security.http.ssl和xpack.security.transport.ssl后的子配置需要空一格,遵循yml的格式要求
-- 如果不需要后续的http证书认证或者用户密码认证可以将以下参数的值改为false
-
-```yaml
-xpack.security.http.ssl:
- enabled: false
-xpack.security.transport.ssl:
- enabled: false
-```
-
-- 如果后续在业务场景中遇到了跨域的问题,解决跨域的问题添加以下参数
-
-```yaml
-http.cors.enabled: true
-http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
-```
-
-### 9. 参数解释
-
-```shell
-cluster.name: xingdian-es
-含义: 指定Elasticsearch集群的名称。在此例中,集群名为xingdian-es,所有想要加入此集群的节点都应配置相同的集群名称。
-
-node.name: es-1.xingdian.com
-含义: 设置单个节点的名称。这里将节点命名为es-1.xingdian.com,有助于标识和管理集群中的不同节点。
-
-path.data: /usr/local/es/data
-含义: 指定Elasticsearch存储数据的路径。数据文件将保存在/usr/local/es/data目录下。
-
-path.logs: /usr/local/es/logs
-含义: 配置日志文件的存放路径,即日志将会被写入到/usr/local/es/logs目录中。
-
-network.host: 0.0.0.0
-含义: 设置监听所有可用网络接口的IP地址,允许Elasticsearch从任何网络接口接收连接请求。
-
-http.port: 9200
-含义: 指定HTTP服务监听的端口号,这里是9200,是Elasticsearch默认的HTTP访问端口。
-
-discovery.seed_hosts: ["es-1.xingdian.com","es-2.xingdian.com","es-3.xingdian.com"]
-含义: 列出初始种子节点的地址,用于集群启动时发现其他节点。这有助于新节点加入或现有节点重启后找到集群。
-
-cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["es-1.xingdian.com","es-2.xingdian.com","es-3.xingdian.com"]
-含义: 在初次启动或集群完全重启后,指定哪些节点可以成为初始主节点,用于选举过程。
-
-xpack.security.enabled: true
-含义: 启用X-Pack安全特性,提供认证、授权、加密传输等功能,增强Elasticsearch的安全性。
-
-xpack.security.http.ssl.enabled: true
-含义: 开启HTTP通信的SSL加密,确保客户端与Elasticsearch之间的数据传输安全。
-
-keystore.path, truststore.path, keystore.password, truststore.password
-含义: 分别指定了SSL证书的存放路径和密钥库、信任库的密码。这些设置用于保护SSL连接的密钥和信任信息。
-
-http.host: [local, site]
-含义: 指定HTTP服务可以绑定的主机名,_local_表示绑定本地主机,_site_允许绑定所有公开站点地址。
-
-ingest.geoip.downloader.enabled: false
-含义: 禁用了GeoIP数据库的自动下载功能。GeoIP用于地理定位,禁用后需要手动管理数据库更新。
-
-xpack.security.http.ssl.client_authentication: none
-含义: 设置客户端认证方式为“无”,意味着HTTP客户端连接到Elasticsearch时不需要提供证书进行认证。
-```
-
-### 10. JVM参数调整
-
-```bash
-[root@elasticsearch1 config]# vim jvm.options
--Xms2g
--Xmx2g
-```
-
-注意:该值为真实内存的1/2
-
-### 11. 启动集群
-
-```bash
-[elasticsearch@elasticsearch1/2/3 ~]$ nohup /usr/local/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch &
-```
-
-### 12. 设置登录密码
-
-```bash
-[elasticsearch@elasticsearch1/2/3 ~]$ /usr/local/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-reset-password -u elastic -i
-warning: ignoring JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/elasticsearch/jdk; using bundled JDK
-This tool will reset the password of the [elastic] user.
-You will be prompted to enter the password.
-Please confirm that you would like to continue [y/N]y
-
-
-Enter password for [elastic]:
-Re-enter password for [elastic]:
-Password for the [elastic] user successfully reset.
-```
-
-### 13. 浏览器访问
-
-https://192.168.159.131:9200
-
-
-
-
-
-### 14. 插件访问
-
-Multi Elasticsearch Heads
-
-
-
-Elasticsearch Tools
-
-
-
-Elasticvue
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-## 四:基本概念
-
-### 1. elasticsearch 与传统数据的区别
-
- 一个ES集群可以包含多个索引(数据库),每个索引又包含了很多类型(表),类型中包含了很多文档(行),每个文档使用 JSON 格式存储数据,包含了很多字段(列)。
-
-| 关系型数据库 | Elasticsearch |
-| :-------------: | :-----------------: |
-| 数据库>表>行>列 | 索引>类型>文档>字段 |
-
-### 2. 基本概念
-
-**索引(index)**
-
- ES将数据存储于一个或多个索引中。类比传统的关系型数据库领域来说,索引相当于SQL中的一个数据库,索引由其名称(必须为全小写字符)进行标识。一个ES集群中可以按需创建任意数目的索引。
-
-**类型(type)**
-
- 类型是索引内部的逻辑分区(category/partition),一个索引内部可定义一个或多个类型(type)。类比传统的关系型数据库领域来说,类型相当于“表”。
-
-**文档(document)**
-
- 文档是索引和搜索的原子单位,它是包含了一个或多个域(Field)的容器,每个域拥有一个名字及一个或多个值,有多个值的域通常称为“多值域”,文档基于JSON格式进行表示。每个文档可以存储不同的域集,但同一类型下的文档至应该有某种程度上的相似之处。类比传统的关系型数据库领域来说,类型相当于“行”。
-
-**集群(cluster)**
-
- 一个或者多个拥有相同cluster.name配置的节点组成, 它们共同承担数据和负载的压力。
-
-**节点(node)**
-
- 一个运行中的 Elasticsearch 实例称为一个节点。es中的节点分为三种类型:
-
-- 主节点:负责管理集群范围内的所有变更,例如增加、删除索引,或者增加、删除节点等。 主节点并不需要涉及到文档级别的变更和搜索等操作。可以通过属性`node.master`进行设置。
-- 数据节点:存储数据和其对应的倒排索引。默认每一个节点都是数据节点(包括主节点),可以通过`node.data`属性进行设置。
-- 协调节点:如果`node.master`和`node.data`属性均为false,则此节点称为协调节点,用来响应客户请求,均衡每个节点的负载。
-
-注意:
-
- 使用index和doc_type来组织数据。doc_type中的每条数据称为一个document,是一个JSON Object。
-
- ES分布式搜索,传统数据库遍历式搜索
-
-**分片(Shards)**
-
- 分片是Elasticsearch进行数据分布和扩展的基础。每个索引都可以被分割成多个分片,每个分片其实是一个独立的索引。分片使得Elasticsearch可以把巨大的数据集分散存储在多个节点上,这样可以实现:
-
-- 水平扩展:随着数据量的增加,可以通过增加更多的节点来分摊数据和负载,从而提高处理能力
-- 提升性能:搜索操作可以并行在多个分片上执行,每个分片处理的速度更快,整体搜索性能得以提升
-
-**副本(Replicas)**
-
- 副本是分片的复制,主要用于提高数据的可用性和搜索查询的并发处理能力。每个分片都可以有一个或多个副本,这些副本分布在不同的节点上,从而提供了:
-
-- 数据可用性:当某个节点发生故障时,该节点上的分片如果有副本存在于其他节点上,那么这些副本可以保证数据不会丢失,并且服务还可以继续运行。
-- 负载均衡:读取操作(如搜索请求)可以在所有副本之间进行负载均衡,这样可以提高查询的吞吐量和响应速度。
-
-**定义分片和副本**
-
- 创建索引时指定分片和副本数
-
- 当您通过Elasticsearch的REST API创建一个新的索引时,可以在请求体中使用settings部分来指定该索引的分片数(number_of_shards)和副本数(number_of_replicas)。以下是一个具体的示例:
-
-```json
-PUT /my_index
-{
- "settings": {
- "index": {
- "number_of_shards": 3, # 指定该索引将有3个主分片
- "number_of_replicas": 2 # 每个主分片将有2个副本分片
- }
- }
-}
-```
-
-
-
- 这个例子中,PUT /my_index是创建名为my_index的索引的请求。在请求体中,settings部分指出这个索引将被分成3个主分片,并且每个主分片将会有2个副本分片。这意味着,总共会有9个分片(3个主分片 + 6个副本分片)被分布在集群中。
-
-- 主分片数量:一旦索引被创建,其主分片的数量就无法更改。因此,在创建时应谨慎选择合适的分片数量。
-- 副本数量:与主分片数量不同,副本的数量是可以动态调整的。如果需要更多的数据冗余或查询吞吐量,可以增加副本的数量。
-- 伸缩性与性能:选择分片和副本的数量时需要考虑数据量、查询负载和集群的硬件资源。过多的分片可能会增加集群的管理开销,而过少的分片可能会限制数据和查询的伸缩性。
-
-分片数的确定
-
-- 数据量预估:估计索引的总数据量大小。一般来说,每个分片处理20GB到50GB数据是比较理想的。这不是固定规则,但可以作为一个起点。
-- 硬件资源:考虑你的硬件资源,尤其是内存和CPU。分片越多,消耗的资源也越多。确保你的Elasticsearch集群有足够的资源来处理这些分片。
-- 写入吞吐量:如果你的应用会有大量的写入操作,更多的分片可能有助于提高写入性能,因为可以并行写入多个分片。
-- 查询性能:更多的分片意味着查询可以并行于更多的分片上执行,这可能会提高查询性能。但是,如果每个查询都要访问大多数分片,那么管理过多的分片会减慢查询速度。
-
-副本数的确定
-
-- 数据可用性:至少有一个副本可以确保当某个节点失败时,数据不会丢失,并且Elasticsearch服务仍然可用。
-- 读取性能:更多的副本意味着更高的读取吞吐量,因为读取请求可以在多个副本之间分配。如果你的应用主要是读取密集型的,增加副本数可以提高查询性能。
-- 集群负载:考虑集群的整体负载。增加副本会提高数据冗余和读取性能,但也会增加存储需求和网络流量,因此需要确保你的硬件资源可以支持。
-
-## 五:Elasticsearch 集群架构
-
-### 1. Discovery 发现
-
- 发现是集群形成模块寻找其他节点以形成集群的过程。当您启动 Elasticsearch 节点或节点认为主节点发生故障时,此过程将运行,并持续到找到主节点或选出新的主节点为止。
-
- 此过程分为两个阶段:首先,每个节点通过连接到每个地址并尝试识别其所连接的节点以及验证其是否符合主节点资格来探测种子地址。其次,如果成功,它将与远程节点共享其所有已知符合主节点资格的对等节点的列表,然后远程节点依次与其对等节点进行响应。然后,节点探测它刚刚发现的所有新节点,请求其对等节点,依此类推。
-
- 如果节点不符合主节点资格,则它将继续此发现过程,直到发现选举的主节点。如果没有发现选举的主节点,则节点将重试,之后`discovery.find_peers_interval`默认为`1s` 。
-
- 如果节点符合主节点条件,则它会继续此发现过程,直到发现当选主节点或发现足够多的无主主节点来完成选举。如果上述两种情况都发生得不够快,则节点将重试,之后`discovery.find_peers_interval`默认为`1s`。
-
- 一旦主节点被选出,它通常会继续担任主节点,直到被故意停止。如果 故障检测确定集群出现故障,它也可能会停止担任主节点。当某个节点不再是主节点时,它会再次开始发现过程。
-
-### 2. 种子主机提供商
-
-默认情况下,集群形成模块提供两个种子主机提供程序来配置种子节点列表
-
-- 基于设置的种子主机提供程序
-- 基于文件的种子主机提供程序
-
- 种子主机提供程序使用设置进行配置`discovery.seed_providers` ,默认为基于设置的主机提供程序
-
-**基于设置的种子主机提供商:**
-
- 基于设置的种子主机提供程序使用节点设置来配置种子节点地址的静态列表。这些地址可以作为主机名或 IP 地址指定;在每轮发现期间,指定为主机名的主机都会解析为 IP 地址。
-
-```yml
-discovery.seed_hosts:
- - 192.168.159.131:9200
- - 192.168.159.132:9200
- - 192.168.159.133:9200
-
-或者:
-discovery.seed_hosts: ["192.168.159.131:9200","192.168.159.132:9200","192.168.159.133:9200"]
-```
-
-**基于文件的种子主机提供商:**
-
- 基于文件的种子主机提供程序通过外部文件配置主机列表。Elasticsearch会在文件更改时重新加载此文件,这样种子节点列表就可以动态更改,而无需重新启动每个节点。例如,这为在Docker容器中运行的 Elasticsearch 实例提供了一种方便的机制,当节点启动时可能不知道这些IP地址时,可以动态地为其提供要连接的IP地址列表。
-
-```yaml
-discovery.seed_providers: file
-```
-
- 然后按照下面描述的格式创建一个文件`$ES_PATH_CONF/unicast_hosts.txt`。每当对文件进行更改时,Elasticsearch都会获取新的更改并使用新的主机列表。
-
- 该`unicast_hosts.txt`文件每行包含一个节点条目。每个节点条目由主机(主机名或 IP 地址)和一个可选的传输端口号组成。如果指定了端口号,它必须紧跟在主机之后(在同一行上)。
-
- 允许使用主机名代替 IP 地址,并由 DNS 解析,如上所述。IPv6 地址必须在括号中给出,如果需要,端口号也应放在括号后面
-
-```bash
-cat $ES_PATH_CONF/unicast_hosts.txt
-10.10.10.5
-10.10.10.6:9305
-10.10.10.5:10005
-# an IPv6 address
-[2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334]:9301
-```
-
-### 3. 基于集群的决策
-
- 选举主节点和更改集群状态是符合主节点条件的节点必须协同执行的两个基本任务。即使某些节点发生故障,这些活动也必须能够稳健地运行。Elasticsearch 通过在收到来自法定人数(集群中符合主节点条件的节点的子集)的响应后将每个操作视为成功来实现这种稳健性。仅要求一部分节点响应的优点是,这意味着某些节点可以发生故障而不会阻止集群继续运行。法定人数是经过精心选择的,即集群被分成两部分,以至于每个部分可能做出与另一部分不一致的决策。
-
- Elasticsearch 允许您向正在运行的集群添加和删除符合主节点条件的节点。在许多情况下,您只需根据需要启动或停止节点即可完成此操作。
-
- 随着节点的添加或删除,Elasticsearch 通过更新集群的**投票配置**来保持最佳容错水平,投票配置是一组符合主节点条件的节点,在做出诸如选举新主节点或提交新集群状态等决策时,这些节点的响应会被计算在内。只有在投票配置中超过一半的节点做出响应后,才会做出决策。通常,投票配置与集群中当前所有符合主节点条件的节点集相同。但是,在某些情况下,它们可能会有所不同。
-
- 为了确保集群保持可用,不能同时停止投票配置中的一半或更多节点。只要超过一半的投票节点可用,集群仍可正常工作。这意味着,如果有三个或四个主节点,集群可以容忍其中一个不可用。如果有两个或更少的主节点,它们必须全部保持可用。
-
- 如果您同时停止投票配置中的一半或更多节点,则集群将不可用,直到您使足够多的节点重新联机以再次形成法定人数。当集群不可用时,任何剩余节点都会在其日志中报告它们无法发现或选举主节点。
-
-### 4. 主节点选举
-
- Elasticsearch使用选举流程来商定选举的主节点,无论是在启动时还是在现有选举主节点发生故障时。任何符合主节点条件的节点都可以启动选举,通常第一次选举将会成功。只有当两个节点恰好同时开始选举时,选举才会失败,因此每个节点都会随机安排选举以降低发生这种情况的概率。节点将重试选举,直到选出主节点,如果失败则放弃,以便最终选举能够成功(概率任意高)。主节点选举的安排由主节点选举设置控制。
-
-### 5. 投票配置
-
- 每个 Elasticsearch 集群都有一个投票配置,它是一组 符合主节点条件的节点,在做出诸如选举新主节点或提交新集群状态等决策时,这些节点的响应会被计入。只有在投票配置中的大多数节点(超过一半)响应后,才会做出决策。通常,投票配置与集群中当前所有符合主节点条件的节点集相同。但是,在某些情况下,它们可能会有所不同。
-
- 较大的投票配置通常更具弹性,因此 Elasticsearch 通常倾向于在符合主节点资格的节点加入集群后将其添加到投票配置中。同样,如果投票配置中的节点离开集群,并且集群中还有另一个不符合主节点资格的节点不在投票配置中,则最好交换这两个节点。因此,投票配置的大小保持不变,但其弹性会增加。
-
- 在节点离开集群后自动从投票配置中删除节点并不是那么简单。不同的策略有不同的优点和缺点,可以使用设置来控制投票配置是否自动`cluster.auto_shrink_voting_configuration`
-
- 如果`cluster.auto_shrink_voting_configuration`设置为`true`(这是默认值和推荐值)并且集群中至少有三个主合格节点,则只要除一个主合格节点之外的所有节点都健康,Elasticsearch 仍然能够处理集群状态更新
-
- 在某些情况下,Elasticsearch 可能会容忍多个节点丢失,但这并不能保证在所有故障序列下都能做到。如果设置`cluster.auto_shrink_voting_configuration`为`false`,则必须手动从投票配置中移除已离开的节点。
-
-配置参数如下:
-
-```
-cluster.auto_shrink_voting_configuration
-(动态)控制投票配置是否自动删除已离开的节点(只要它仍包含至少 3 个节点)。默认值为true。如果设置为,投票配置永远不会自动缩小,您必须使用投票配置排除 APIfalse手动删除已离开的节点 。
-
-cluster.election.back_off_time
-(静态)设置每次选举失败时选举前等待时间的上限增加量。请注意,这是线性退避。默认值为 100ms。更改此设置(默认设置)可能会导致您的集群无法选举主节点。
-
-cluster.election.duration
-(静态)设置每次选举允许花费多长时间,之后节点才会认为选举失败并安排重试。默认值为500ms。更改此设置可能会导致您的集群无法选举出主节点。
-
-cluster.election.initial_timeout
-(静态)设置节点在首次尝试选举之前(或当选主节点失败后)等待的时间上限。默认值为 100ms。更改此设置(默认设置)可能会导致您的集群无法选举主节点。
-
-cluster.election.max_timeout
-(静态)设置节点在尝试首次选举之前等待时间的最大上限,以便长时间持续的网络分区不会导致选举过于稀疏。默认值为10s。更改此设置(默认设置)可能会导致您的集群无法选举主节点。
-
-cluster.fault_detection.follower_check.interval
-(静态)设置当选主节点在集群中每个其他节点的跟随节点检查之间等待的时间。默认为1s。更改此设置(默认设置除外)可能会导致集群变得不稳定。
-
-cluster.fault_detection.follower_check.timeout
-(静态)设置当选主节点等待跟随者检查响应的时间,超过该时间则认为主节点失败。默认为10s。更改此设置可能会导致集群变得不稳定。
-
-cluster.fault_detection.follower_check.retry_count
-(静态)设置每个节点必须发生多少次连续的跟随者检查失败,当选主节点才会认为该节点有故障并将其从集群中移除。默认为3。更改此设置可能会导致集群变得不稳定。
-
-cluster.fault_detection.leader_check.interval
-(静态)设置每个节点在检查当选主节点之间等待的时间。默认为 1s。更改此设置可能会导致集群变得不稳定。
-
-cluster.fault_detection.leader_check.timeout
-(静态)设置每个节点等待当选主节点对领导者检查的响应的时间,超过该时间则认为主节点已发生故障。默认为10s。更改此设置可能会导致集群变得不稳定。
-
-cluster.fault_detection.leader_check.retry_count
-(静态)设置必须发生多少次连续的领导者检查失败,节点才会认为当选主节点有故障,并尝试查找或选举新主节点。默认为3。更改此设置(默认设置)可能会导致集群变得不稳定。
-
-cluster.follower_lag.timeout
-(静态)设置主节点等待从滞后节点接收集群状态更新确认的时间。默认值为90s。如果节点在此时间段内未成功应用集群状态更新,则该节点被视为发生故障并从集群中删除。请参阅 发布集群状态。
-
-cluster.max_voting_config_exclusions
-(动态)设置一次投票配置排除的数量限制。默认值为10。请参阅在集群中添加和删除节点。
-
-cluster.publish.info_timeout
-(静态)设置主节点等待每个集群状态更新完全发布到所有节点的时间,然后记录一条消息,表明某些节点响应缓慢。默认值为10s。
-
-cluster.publish.timeout
-(静态)设置主节点等待每个集群状态更新完全发布到所有节点的时间,除非discovery.type设置为 single-node。默认值为30s。请参阅发布集群状态。
-
-cluster.discovery_configuration_check.interval
-(静态)设置某些检查的间隔,这些检查将记录有关不正确的发现配置的警告。默认值为30s。
-
-cluster.join_validation.cache_timeout
-(静态)当一个节点请求加入集群时,当选的主节点会向其发送一份最新集群状态的副本,以检测可能阻止新节点加入集群的某些问题。主节点会缓存其发送的状态,如果另一个节点不久后加入集群,则使用缓存的状态。此设置控制主节点等待清除此缓存的时间。默认为60s。
-```
-
- 通常,集群中的主节点数应为奇数。如果为偶数,Elasticsearch 会将其中一个节点排除在投票配置之外,以确保其大小为奇数
-
-### 6. 引导集群
-
- 首次启动 Elasticsearch 集群时,需要在集群中的一个或多个主节点上明确定义初始主节点集。这称为集群引导。这仅在集群首次启动时才需要。加入正在运行的集群的新启动节点从集群的选定主节点获取此信息。
-
- `cluster.initial_master_nodes`初始的符合主节点资格的节点集在设置中定义 。这应该设置为一个列表,其中包含每个符合主节点资格的以下项目之一:
-
-- 节点名称
-- node.name如果未设置,则默认为节点的主机名
-
- 集群形成后,`cluster.initial_master_nodes`从每个节点的配置中删除该设置。不应为非主节点、加入现有集群的主节点或正在重新启动的节点设置该设置。
-
-**配置使用如下:**
-
- 创建新集群的最简单方法是选择一个主节点,该节点将自行引导到单节点集群中,然后所有其他节点将加入该集群。
-
-```yaml
-cluster.initial_master_nodes: elasticsearch1
-```
-
- 对于容错集群引导,请使用所有符合主节点条件的节点。例如,如果您的集群有 3 个符合主节点条件的节点,节点名称`elasticsearch1`为,`elasticsearch2`则按`elasticsearch3`如下方式配置它们:
-
-```yaml
-cluster.initial_master_nodes:
- - elasticsearch1
- - elasticsearch2
- - elasticsearch3
-```
-
-**选择集群名称:**
-
- 此`cluster.name`设置允许您创建多个彼此独立的集群。节点在首次连接时会验证它们是否同意其集群名称,并且 Elasticsearch 只会从具有相同集群名称的节点组成集群。集群名称的默认值为elasticsearch,但建议将其更改为反映集群的逻辑名称。
-
-**开发模式下的自动引导:**
-
- 默认情况下,每个节点在首次启动时都会自动引导到单节点集群。如果配置了以下任何设置,则不会进行自动引导:
-
-```
-discovery.seed_providers
-discovery.seed_hosts
-cluster.initial_master_nodes
-```
-
-注意:
-
- 一旦 Elasticsearch 节点加入现有集群或引导新集群,它就不会再加入其他集群。Elasticsearch 不会在集群形成后将单独的集群合并在一起,即使您随后尝试将所有节点配置为单个集群。这是因为没有办法将这些单独的集群合并在一起而不丢失数据。
-
-## 六:IK 分词器
-
-### 1. 简介
-
- ES IK分词器是一种基于中文文本的分词器,它是Elasticsearch中文分词的一种实现。它采用了自然语言处理技术,可以将中文文本进行切分,抽取出其中的词汇,从而提高搜索引擎对中文文本的搜索和检索效率。
-
- ES IK分词器的原理是采用了一种叫做“正向最大匹配”(Forward Maximum Matching,简称FMM)和“逆向最大匹配”(Backward Maximum Matching,简称BMM)的分词算法,通过对文本进行多次切分,最终确定最优的分词结果。
-
- ES IK分词器可以用于各种中文文本处理应用,包括搜索引擎、文本挖掘、信息检索等。它支持多种分词模式,包括最细粒度切分、智能切分和最大切分等模式,可以根据具体应用场景进行灵活配置。
-
-### 2. 分类
-
-**细粒度分词模式(ik_max_word):**
-
-- 在这种模式下,IK分词器会尽可能地按照词典中的词语进行最大长度匹配,将文本切分成连续的词语序列
-- 这种模式适用于对文本进行细致的切分,尽可能将句子切分为最小的词语单元,获得更加精确的分词结果
-
-**智能分词模式(ik_smart):**
-
-- 在智能切分模式下,IK分词器会结合词典匹配和机器学习算法,根据上下文信息分词,保留词语的完整性
-- 这种模式能够更好地处理一些特殊情况,如未登录词和新词等,提高了分词的准确性和适用性
-
-### 3. 下载地址
-
-https://github.com/infinilabs/analysis-ik/releases/tag/Latest
-
-### 4. 安装插件
-
-注意:
-
-- 安装的插件版本需要跟elasticsearch的版本一致,否则无法安装或报错
-- 安装完成后重启elasticsearch
-
-```bash
-[elasticsearch@elasticsearch1 ~]$ /usr/local/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-plugin install https://get.infini.cloud/elasticsearch/analysis-ik/8.13.4
-warning: ignoring JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/elasticsearch/jdk; using bundled JDK
--> Installing https://get.infini.cloud/elasticsearch/analysis-ik/8.13.4
--> Downloading https://get.infini.cloud/elasticsearch/analysis-ik/8.13.4
-@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@
-@ WARNING: plugin requires additional permissions @
-@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@
-* java.net.SocketPermission * connect,resolve
-See https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/technotes/guides/security/permissions.html
-for descriptions of what these permissions allow and the associated risks.
-
-Continue with installation? [y/N]y
--> Installed analysis-ik
-```
-
-### 5. 项目需求
-
-如果对应的项目使用到了ES IK插件,我们需要在ES集群中构建IK环境
-
-## 七:冷热温节点部署
-
-### 1. 简介
-
- 在某些大规模数据分析场景(比如时间数据分析),可以采用此架构:基于时间创建 index,然后持续地把温/冷数据迁移到相应的数据节点。
-
- 专有主节点:由于不保存数据,也就不参与索引和查询操作,不会被长 GC 干扰,负载可以保持在较低水平,能极大提高集群的稳定性
-
- 热数据节点:保存近期的 index,承担最频繁的写入和查询操作,可以配置较高的资源,如超高性能主机及硬盘。可以在集群配置参数里 Elasticsearch 节点的参数`node.attr.data`(热)做修改,默认为 `hot`
-
- 温/冷数据节点:保存只读 index,会接收少量的查询请求,可以配置较低的资源。可以在集群配置参数里 Elasticsearch 节点的参数 `node.attr.data`(温)和` node.attr.data`(冷)做修改,默认为 `warm`和` cold`
-
-### 2. 准备工作
-
-前期部署参考:三:集群部署
-
-### 3. 修改配置
-
-es-1-data_hot
-
-```bash
-[elasticsearch@elasticsearch1 ~]$ vim /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/elasticsearch.yml
-cluster.name: elasticsearch
-node.name: elasticsearch1
-path.data: /usr/local/elasticsearch/data
-path.logs: /usr/local/elasticsearch/logs
-network.host: 0.0.0.0
-http.port: 9200
-node.roles: [data_hot,data_content,master,ingest]
-discovery.seed_hosts: ["192.168.159.131:9200", "192.168.159.132:9200","192.168.159.133:9200"]
-cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["elasticsearch1"]
-xpack.security.enabled: true
-xpack.security.enrollment.enabled: true
-xpack.security.http.ssl:
- enabled: true
- keystore.path: /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs/http.p12
- truststore.path: /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs/http.p12
-xpack.security.transport.ssl:
- enabled: true
- verification_mode: certificate
- keystore.path: /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs/elastic-certificates.p12
- truststore.path: /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs/elastic-certificates.p12
-http.host: [_local_, _site_]
-ingest.geoip.downloader.enabled: false
-xpack.security.http.ssl.client_authentication: none
-http.cors.enabled: true
-http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
-```
-
-es-2-data_warm
-
-```bash
-[elasticsearch@elasticsearch2 ~]$ vim /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/elasticsearch.yml
-cluster.name: elasticsearch
-node.name: elasticsearch2
-path.data: /usr/local/elasticsearch/data
-path.logs: /usr/local/elasticsearch/logs
-network.host: 0.0.0.0
-http.port: 9200
-node.roles: [data_warm, data_content, master, ingest]
-discovery.seed_hosts: ["192.168.159.131:9200", "192.168.159.132:9200","192.168.159.133:9200"]
-cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["elasticsearch1"]
-xpack.security.enabled: true
-xpack.security.enrollment.enabled: true
-xpack.security.http.ssl:
- enabled: true
- keystore.path: /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs/http.p12
- truststore.path: /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs/http.p12
-xpack.security.transport.ssl:
- enabled: true
- verification_mode: certificate
- keystore.path: /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs/elastic-certificates.p12
- truststore.path: /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs/elastic-certificates.p12
-http.host: [_local_, _site_]
-ingest.geoip.downloader.enabled: false
-xpack.security.http.ssl.client_authentication: none
-http.cors.enabled: true
-http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
-```
-
-es-3-data_cold
-
-```bash
-cluster.name: elasticsearch
-node.name: elasticsearch3
-path.data: /usr/local/elasticsearch/data
-path.logs: /usr/local/elasticsearch/logs
-network.host: 0.0.0.0
-http.port: 9200
-node.roles: [data_cold, data_content, master, ingest]
-discovery.seed_hosts: ["elasticsearch1", "elasticsearch2","elasticsearch3"]
-cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["elasticsearch1"]
-xpack.security.enabled: true
-xpack.security.enrollment.enabled: true
-xpack.security.http.ssl:
- enabled: true
- keystore.path: /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs/http.p12
- truststore.path: /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs/http.p12
-xpack.security.transport.ssl:
- enabled: true
- verification_mode: certificate
- keystore.path: /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs/elastic-certificates.p12
- truststore.path: /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs/elastic-certificates.p12
-http.host: [_local_, _site_]
-ingest.geoip.downloader.enabled: false
-xpack.security.http.ssl.client_authentication: none
-http.cors.enabled: true
-http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
-```
-
-### 4. 启动服务
-
-依次启动所有节点
-
-```bash
-[elasticsearch@elasticsearch1 ~]$ nohup /usr/local/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch &
-[elasticsearch@elasticsearch2 ~]$ nohup /usr/local/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch &
-[elasticsearch@elasticsearch3 ~]$ nohup /usr/local/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch &
-```
-
-### 5. 修改密码
-
-依次修改所有节点
-
-```bash
-[elasticsearch@elasticsearch1 ~]$ /usr/local/es/bin/elasticsearch-reset-password -u elastic -i
-warning: ignoring JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/es/jdk; using bundled JDK
-This tool will reset the password of the [elastic] user.
-You will be prompted to enter the password.
-Please confirm that you would like to continue [y/N]y
-
-
-Enter password for [elastic]:
-Re-enter password for [elastic]:
-Password for the [elastic] user successfully reset.
-```
-
-### 6. 访问验证
-
-```
-GET /_cat/nodes
-```
-
-
-
-### 7. 应用案例
-
-设置特定的索引,分片设置为5
-
-```yaml
-PUT kibana_sample_data_logs_ext
-{
- "settings": {
- "number_of_replicas": 0,
- "number_of_shards": 5
- }
-}
-```
-
-
-
-准备索引数据,首先你得先确保您索引有:wxin
-
-```yaml
-POST _reindex
-{
- "source": {
- "index": "wxin"
- },
- "dest": {
- "index": "kibana_sample_data_logs_ext"
- }
-}
-```
-
-
-
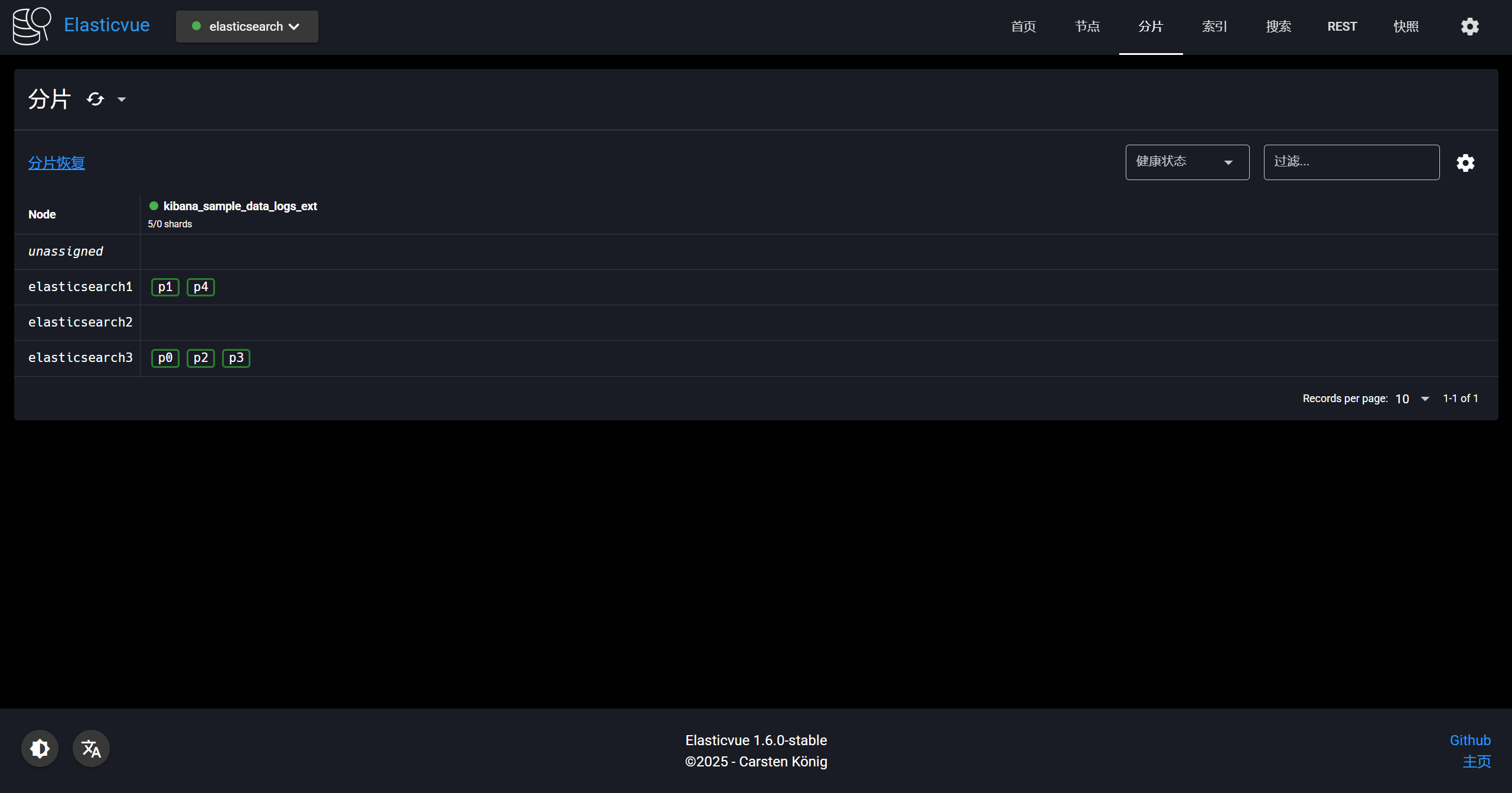
-这是现在的分片情况
-
-
-
-设置索引分片信息,主要参数:index.routing.allocation.include._tier_preference
-
-索引-路由-分配,分配到data_hot节点上,之前我们在配置文件内定义的节点
-
-```yaml
-PUT kibana_sample_data_logs_ext/_settings
-{
- "settings": {
- "index.number_of_replicas": 0,
- "index.routing.allocation.include._tier_preference": "data_hot",
- "index.blocks.write": true
- }
-}
-```
-
-
-
-在查询就能看到分片都在hot节点上了
-
-
+Elasticsearch 集群搭建
+
+------
+
+## 一:环境准备
+
+### 1. 简介
+
+ 部署模式:es集群采用无主模式
+
+ es版本:8.13.4
+
+ jdk版本:使用es内嵌的jdk21,无需额外安装jdk环境
+
+ 操作系统:Centos 7
+
+### 2. 环境
+
+| IP地址 | 主机名 | 角色 |
+| :-------------: | :-------------: | :-------------: |
+| 192.168.159.131 | elasticsearch01 | master&data节点 |
+| 192.168.159.132 | elasticsearch02 | master&data节点 |
+| 192.168.159.133 | elasticsearch03 | master&data节点 |
+
+## 二:服务器配置
+
+### 1. 创建用户
+
+es不能使用root用户进行部署,故创建新用户管理es集群
+
+```bash
+# 添加一个用户 elasticsearch 密码 elasticsearch
+[root@elasticsearch1 ~]# useradd elasticsearch && echo elasticsearch | passwd --stdin elasticsearch
+```
+
+### 2. 本地解析
+
+```bash
+[root@elasticsearch1 ~]# vim /etc/hosts
+192.168.159.131 elasticsearch1
+192.168.159.132 elasticsearch2
+192.168.159.133 elasticsearch3
+```
+
+### 3. 系统优化
+
+优化最大进程数,最大文件打开数,优化虚拟内存
+
+```bash
+[root@elasticsearch1 ~]# vim /etc/security/limits.conf
+* soft nofile 65536
+* hard nofile 131072
+* soft nproc 4096
+* hard nproc 6553
+
+[root@elasticsearch1 ~]# vim /etc/sysctl.conf
+vm.max_map_count=262144
+
+[root@elasticsearch1 ~]# sysctl -p
+vm.max_map_count = 262144
+```
+
+## 三:集群部署
+
+### 1. 获取安装包
+
+官网:[Past Releases of Elastic Stack Software | Elastic](https://www.elastic.co/downloads/past-releases#elasticsearch)
+
+```bash
+[root@elasticsearch1 ~]# wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-8.13.4-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
+```
+
+### 2. 解压安装
+
+```bash
+[root@elasticsearch1 ~]# tar xf elasticsearch-8.13.4-linux-x86_64.tar.gz -C /usr/local/
+[root@elasticsearch1 ~]# mv /usr/local/elasticsearch-8.13.4/ /usr/local/elasticsearch
+[root@elasticsearch1 ~]# chown -R elasticsearch:elasticsearch /usr/local/elasticsearch
+```
+
+### 3. 配置环境变量
+
+```bash
+[root@elasticsearch1 ~]# vim /etc/profile
+JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/elasticsearch/jdk
+ES_HOME=/usr/local/elasticsearch
+PATH=$PATH:$JAVA_HOME/bin:$ES_HOME/bin
+export JAVA_HOME ES_HOME PATH
+
+# 刷新环境变量
+[root@elasticsearch1 ~]# source /etc/profile
+
+[root@elasticsearch1 ~]# java -version
+openjdk version "21.0.2" 2024-01-16
+OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 21.0.2+13-58)
+OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 21.0.2+13-58, mixed mode, sharing)
+```
+
+### 4. 创建目录
+
+目录用来存储数据和存放证书并赋予权限
+
+```bash
+[root@elasticsearch1 ~]# mkdir -p /usr/local/elasticsearch/data
+[root@elasticsearch1 ~]# mkdir -p /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs
+[root@elasticsearch1 ~]# chown -R elasticsearch:elasticsearch /usr/local/elasticsearch/
+```
+
+**注意:截至到目前为止,所有节点服务器的操作都是一致的**
+
+### 5. 签发证书
+
+```bash
+# 在第一台服务器节点 elasticsearch1 设置集群多节点通信密钥
+# 切换用户
+[root@elasticsearch1 ~]# su - elasticsearch
+[elasticsearch@elasticsearch1 ~]$ cd /usr/local/elasticsearch/bin/
+[elasticsearch@elasticsearch1 bin]$ ./elasticsearch-certutil ca
+warning: ignoring JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/elasticsearch/jdk; using bundled JDK
+This tool assists you in the generation of X.509 certificates and certificate
+signing requests for use with SSL/TLS in the Elastic stack.
+
+The 'ca' mode generates a new 'certificate authority'
+This will create a new X.509 certificate and private key that can be used
+to sign certificate when running in 'cert' mode.
+
+Use the 'ca-dn' option if you wish to configure the 'distinguished name'
+of the certificate authority
+
+By default the 'ca' mode produces a single PKCS#12 output file which holds:
+ * The CA certificate
+ * The CA's private key
+
+If you elect to generate PEM format certificates (the -pem option), then the output will
+be a zip file containing individual files for the CA certificate and private key
+
+Please enter the desired output file [elastic-stack-ca.p12]:
+Enter password for elastic-stack-ca.p12 :
+
+# 用 ca 证书签发节点证书,过程中需按三次回车键,生成目录:elasticsearch的home:/usr/local/elasticsearch/
+[elasticsearch@elasticsearch1 bin]$ ./elasticsearch-certutil cert --ca elastic-stack-ca.p12
+...
+If you specify any of the following options:
+ * -pem (PEM formatted output)
+ * -multiple (generate multiple certificates)
+ * -in (generate certificates from an input file)
+then the output will be be a zip file containing individual certificate/key files
+
+Enter password for CA (elastic-stack-ca.p12) :
+Please enter the desired output file [elastic-certificates.p12]:
+Enter password for elastic-certificates.p12 :
+
+Certificates written to /usr/local/elasticsearch/elastic-certificates.p12
+
+This file should be properly secured as it contains the private key for
+your instance.
+This file is a self contained file and can be copied and used 'as is'
+For each Elastic product that you wish to configure, you should copy
+this '.p12' file to the relevant configuration directory
+and then follow the SSL configuration instructions in the product guide.
+
+For client applications, you may only need to copy the CA certificate and
+configure the client to trust this certificate.
+
+# 将生成的证书文件移动到 config/certs 目录中
+[elasticsearch@elasticsearch1 bin]$ cd /usr/local/elasticsearch/
+[elasticsearch@elasticsearch1 elasticsearch]$ ls -l | grep "elastic-"
+-rw------- 1 elasticsearch elasticsearch 3596 4月 29 19:21 elastic-certificates.p12
+-rw------- 1 elasticsearch elasticsearch 2672 4月 29 19:19 elastic-stack-ca.p12
+[elasticsearch@elasticsearch1 elasticsearch]$ mv elastic-certificates.p12 config/certs/
+[elasticsearch@elasticsearch1 elasticsearch]$ mv elastic-stack-ca.p12 config/certs/
+```
+
+### 6. 设置集群多节点HTTP证书
+
+```bash
+[elasticsearch@elasticsearch1 elasticsearch]$ cd /usr/local/elasticsearch/bin/
+[elasticsearch@elasticsearch1 bin]$ ./elasticsearch-certutil http
+warning: ignoring JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/elasticsearch/jdk; using bundled JDK
+
+## Elasticsearch HTTP Certificate Utility
+
+The 'http' command guides you through the process of generating certificates
+for use on the HTTP (Rest) interface for Elasticsearch.
+
+This tool will ask you a number of questions in order to generate the right
+set of files for your needs.
+
+## Do you wish to generate a Certificate Signing Request (CSR)?
+
+A CSR is used when you want your certificate to be created by an existing
+Certificate Authority (CA) that you do not control (that is, you don't have
+access to the keys for that CA).
+
+If you are in a corporate environment with a central security team, then you
+may have an existing Corporate CA that can generate your certificate for you.
+Infrastructure within your organisation may already be configured to trust this
+CA, so it may be easier for clients to connect to Elasticsearch if you use a
+CSR and send that request to the team that controls your CA.
+
+If you choose not to generate a CSR, this tool will generate a new certificate
+for you. That certificate will be signed by a CA under your control. This is a
+quick and easy way to secure your cluster with TLS, but you will need to
+configure all your clients to trust that custom CA.
+######################################################
+# 是否生成CSR,选择 N ,不需要 #
+######################################################
+Generate a CSR? [y/N]N
+
+## Do you have an existing Certificate Authority (CA) key-pair that you wish to use to sign your certificate?
+
+If you have an existing CA certificate and key, then you can use that CA to
+sign your new http certificate. This allows you to use the same CA across
+multiple Elasticsearch clusters which can make it easier to configure clients,
+and may be easier for you to manage.
+
+If you do not have an existing CA, one will be generated for you.
+########################################################
+# 是否使用已经存在的CA证书,选择 y ,因为已经创建签发好了CA #
+########################################################
+Use an existing CA? [y/N]y
+
+## What is the path to your CA?
+
+Please enter the full pathname to the Certificate Authority that you wish to
+use for signing your new http certificate. This can be in PKCS#12 (.p12), JKS
+(.jks) or PEM (.crt, .key, .pem) format.
+######################################################
+# 指定CA证书的路径地址,CA Path:后写绝对路径 #
+######################################################
+CA Path: /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs/elastic-stack-ca.p12
+Reading a PKCS12 keystore requires a password.
+It is possible for the keystore's password to be blank,
+in which case you can simply press at the prompt
+######################################################
+# 设置密钥库的密码,直接 回车 即可 #
+######################################################
+Password for elastic-stack-ca.p12:
+
+## How long should your certificates be valid?
+
+Every certificate has an expiry date. When the expiry date is reached clients
+will stop trusting your certificate and TLS connections will fail.
+
+Best practice suggests that you should either:
+(a) set this to a short duration (90 - 120 days) and have automatic processes
+to generate a new certificate before the old one expires, or
+(b) set it to a longer duration (3 - 5 years) and then perform a manual update
+a few months before it expires.
+
+You may enter the validity period in years (e.g. 3Y), months (e.g. 18M), or days (e.g. 90D)
+######################################################
+# 设置证书的失效时间,这里的y表示年,5y则代表失效时间5年 #
+######################################################
+For how long should your certificate be valid? [5y] 5y
+
+## Do you wish to generate one certificate per node?
+
+If you have multiple nodes in your cluster, then you may choose to generate a
+separate certificate for each of these nodes. Each certificate will have its
+own private key, and will be issued for a specific hostname or IP address.
+
+Alternatively, you may wish to generate a single certificate that is valid
+across all the hostnames or addresses in your cluster.
+
+If all of your nodes will be accessed through a single domain
+(e.g. node01.es.example.com, node02.es.example.com, etc) then you may find it
+simpler to generate one certificate with a wildcard hostname (*.es.example.com)
+and use that across all of your nodes.
+
+However, if you do not have a common domain name, and you expect to add
+additional nodes to your cluster in the future, then you should generate a
+certificate per node so that you can more easily generate new certificates when
+you provision new nodes.
+#########################################################
+# 是否需要为每个节点都生成证书,选择 N 无需每个节点都配置证书#
+#########################################################
+Generate a certificate per node? [y/N]N
+
+## Which hostnames will be used to connect to your nodes?
+
+These hostnames will be added as "DNS" names in the "Subject Alternative Name"
+(SAN) field in your certificate.
+
+You should list every hostname and variant that people will use to connect to
+your cluster over http.
+Do not list IP addresses here, you will be asked to enter them later.
+
+If you wish to use a wildcard certificate (for example *.es.example.com) you
+can enter that here.
+
+Enter all the hostnames that you need, one per line.
+############################################################
+# 输入需连接集群节点主机名信息,一行输入一个IP地址,空行回车结束 #
+############################################################
+When you are done, press once more to move on to the next step.
+
+elasticsearch1
+elasticsearch2
+elasticsearch3
+
+You entered the following hostnames.
+
+ - elasticsearch1
+ - elasticsearch2
+ - elasticsearch3
+
+####################################################
+# 确认以上是否为正确的配置,输入 Y 表示信息正确 #
+####################################################
+Is this correct [Y/n]Y
+
+## Which IP addresses will be used to connect to your nodes?
+
+If your clients will ever connect to your nodes by numeric IP address, then you
+can list these as valid IP "Subject Alternative Name" (SAN) fields in your
+certificate.
+
+If you do not have fixed IP addresses, or not wish to support direct IP access
+to your cluster then you can just press to skip this step.
+
+Enter all the IP addresses that you need, one per line.
+#########################################################
+# 输入需连接集群节点IP信息,一行输入一个IP地址,空行回车结束 #
+#########################################################
+When you are done, press once more to move on to the next step.
+
+192.168.159.131
+192.168.159.132
+192.168.159.133
+
+You entered the following IP addresses.
+
+ - 192.168.159.131
+ - 192.168.159.132
+ - 192.168.159.133
+
+####################################################
+# 确认以上是否为正确的配置,输入 Y 表示信息正确 #
+####################################################
+Is this correct [Y/n]Y
+
+## Other certificate options
+
+The generated certificate will have the following additional configuration
+values. These values have been selected based on a combination of the
+information you have provided above and secure defaults. You should not need to
+change these values unless you have specific requirements.
+
+Key Name: elasticsearch1
+Subject DN: CN=elasticsearch1
+Key Size: 2048
+####################################################
+# 是否要更改以上这些选项,选择 N ,不更改证书选项配置 #
+####################################################
+Do you wish to change any of these options? [y/N]N
+
+## What password do you want for your private key(s)?
+
+Your private key(s) will be stored in a PKCS#12 keystore file named "http.p12".
+This type of keystore is always password protected, but it is possible to use a
+blank password.
+####################################################
+# 是否要给证书加密,不需要加密,两次 回车 即可 #
+####################################################
+If you wish to use a blank password, simply press at the prompt below.
+Provide a password for the "http.p12" file: [ for none]
+
+## Where should we save the generated files?
+
+A number of files will be generated including your private key(s),
+public certificate(s), and sample configuration options for Elastic Stack products.
+
+These files will be included in a single zip archive.
+
+What filename should be used for the output zip file? [/usr/local/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-ssl-http.zip]
+
+Zip file written to /usr/local/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-ssl-http.zip
+```
+
+### 7. 分发证书
+
+```bash
+# 解压
+[elasticsearch@elasticsearch1 bin]$ cd /usr/local/elasticsearch/
+[elasticsearch@elasticsearch1 elasticsearch]$ unzip elasticsearch-ssl-http.zip
+
+# 移动证书
+[elasticsearch@elasticsearch1 elasticsearch]$ mv ./elasticsearch/http.p12 config/certs/
+[elasticsearch@elasticsearch1 elasticsearch]$ mv ./kibana/elasticsearch-ca.pem config/certs/
+
+# 将证书分发到其他节点02 03
+[elasticsearch@elasticsearch1 elasticsearch]$ exit
+登出
+[root@elasticsearch1 ~]# cd /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs/
+[root@elasticsearch1 certs]# scp ./* elasticsearch2:/usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs/
+[root@elasticsearch1 certs]# scp ./* elasticsearch3:/usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs/
+
+# 修改属主属组
+[root@elasticsearch2/3 ~]#chown -R /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs/*
+```
+
+### 8. 修改配置
+
+```bash
+[root@elasticsearch1/2/3 certs]# cd /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/
+[root@elasticsearch1/2/3 config]# vim elasticsearch.yml
+cluster.name: elasticsearch
+node.name: elasticsearch1
+path.data: /usr/local/elasticsearch/data
+path.logs: /usr/local/elasticsearch/logs
+network.host: 0.0.0.0
+http.port: 9200
+discovery.seed_hosts: ["192.168.159.131:9200", "192.168.159.132:9200","192.168.159.133:9200"]
+cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["elasticsearch1", "elasticsearch2","elasticsearch3"]
+xpack.security.enabled: true
+xpack.security.enrollment.enabled: true
+xpack.security.http.ssl:
+ enabled: true
+ keystore.path: /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs/http.p12
+ keystore.password: 123456 # 如果生成证书时设置了密码则要添加密码配置
+ truststore.path: /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs/http.p12
+ truststore.password: 123456 # 如果生成证书时设置了密码则要添加密码配置
+xpack.security.transport.ssl:
+ enabled: true
+ verification_mode: certificate
+ keystore.path: /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs/elastic-certificates.p12
+ keystore.password: 123456 # 如果生成证书时设置了密码则要添加密码配置
+ truststore.path: /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs/elastic-certificates.p12
+ truststore.password: 123456 # 如果生成证书时设置了密码则要添加密码配置
+http.host: [_local_, _site_]
+ingest.geoip.downloader.enabled: false
+xpack.security.http.ssl.client_authentication: none
+```
+
+注意:
+
+- xpack.security.http.ssl和xpack.security.transport.ssl后的子配置需要空一格,遵循yml的格式要求
+- 如果不需要后续的http证书认证或者用户密码认证可以将以下参数的值改为false
+
+```yaml
+xpack.security.http.ssl:
+ enabled: false
+xpack.security.transport.ssl:
+ enabled: false
+```
+
+- 如果后续在业务场景中遇到了跨域的问题,解决跨域的问题添加以下参数
+
+```yaml
+http.cors.enabled: true
+http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
+```
+
+### 9. 参数解释
+
+```shell
+cluster.name: xingdian-es
+含义: 指定Elasticsearch集群的名称。在此例中,集群名为xingdian-es,所有想要加入此集群的节点都应配置相同的集群名称。
+
+node.name: es-1.xingdian.com
+含义: 设置单个节点的名称。这里将节点命名为es-1.xingdian.com,有助于标识和管理集群中的不同节点。
+
+path.data: /usr/local/es/data
+含义: 指定Elasticsearch存储数据的路径。数据文件将保存在/usr/local/es/data目录下。
+
+path.logs: /usr/local/es/logs
+含义: 配置日志文件的存放路径,即日志将会被写入到/usr/local/es/logs目录中。
+
+network.host: 0.0.0.0
+含义: 设置监听所有可用网络接口的IP地址,允许Elasticsearch从任何网络接口接收连接请求。
+
+http.port: 9200
+含义: 指定HTTP服务监听的端口号,这里是9200,是Elasticsearch默认的HTTP访问端口。
+
+discovery.seed_hosts: ["es-1.xingdian.com","es-2.xingdian.com","es-3.xingdian.com"]
+含义: 列出初始种子节点的地址,用于集群启动时发现其他节点。这有助于新节点加入或现有节点重启后找到集群。
+
+cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["es-1.xingdian.com","es-2.xingdian.com","es-3.xingdian.com"]
+含义: 在初次启动或集群完全重启后,指定哪些节点可以成为初始主节点,用于选举过程。
+
+xpack.security.enabled: true
+含义: 启用X-Pack安全特性,提供认证、授权、加密传输等功能,增强Elasticsearch的安全性。
+
+xpack.security.http.ssl.enabled: true
+含义: 开启HTTP通信的SSL加密,确保客户端与Elasticsearch之间的数据传输安全。
+
+keystore.path, truststore.path, keystore.password, truststore.password
+含义: 分别指定了SSL证书的存放路径和密钥库、信任库的密码。这些设置用于保护SSL连接的密钥和信任信息。
+
+http.host: [local, site]
+含义: 指定HTTP服务可以绑定的主机名,_local_表示绑定本地主机,_site_允许绑定所有公开站点地址。
+
+ingest.geoip.downloader.enabled: false
+含义: 禁用了GeoIP数据库的自动下载功能。GeoIP用于地理定位,禁用后需要手动管理数据库更新。
+
+xpack.security.http.ssl.client_authentication: none
+含义: 设置客户端认证方式为“无”,意味着HTTP客户端连接到Elasticsearch时不需要提供证书进行认证。
+```
+
+### 10. JVM参数调整
+
+```bash
+[root@elasticsearch1 config]# vim jvm.options
+-Xms2g
+-Xmx2g
+```
+
+注意:该值为真实内存的1/2
+
+### 11. 启动集群
+
+```bash
+[elasticsearch@elasticsearch1/2/3 ~]$ nohup /usr/local/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch &
+```
+
+### 12. 设置登录密码
+
+```bash
+[elasticsearch@elasticsearch1/2/3 ~]$ /usr/local/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-reset-password -u elastic -i
+warning: ignoring JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/elasticsearch/jdk; using bundled JDK
+This tool will reset the password of the [elastic] user.
+You will be prompted to enter the password.
+Please confirm that you would like to continue [y/N]y
+
+
+Enter password for [elastic]:
+Re-enter password for [elastic]:
+Password for the [elastic] user successfully reset.
+```
+
+### 13. 浏览器访问
+
+https://192.168.159.131:9200
+
+
+
+
+
+### 14. 插件访问
+
+Multi Elasticsearch Heads
+
+
+
+Elasticsearch Tools
+
+
+
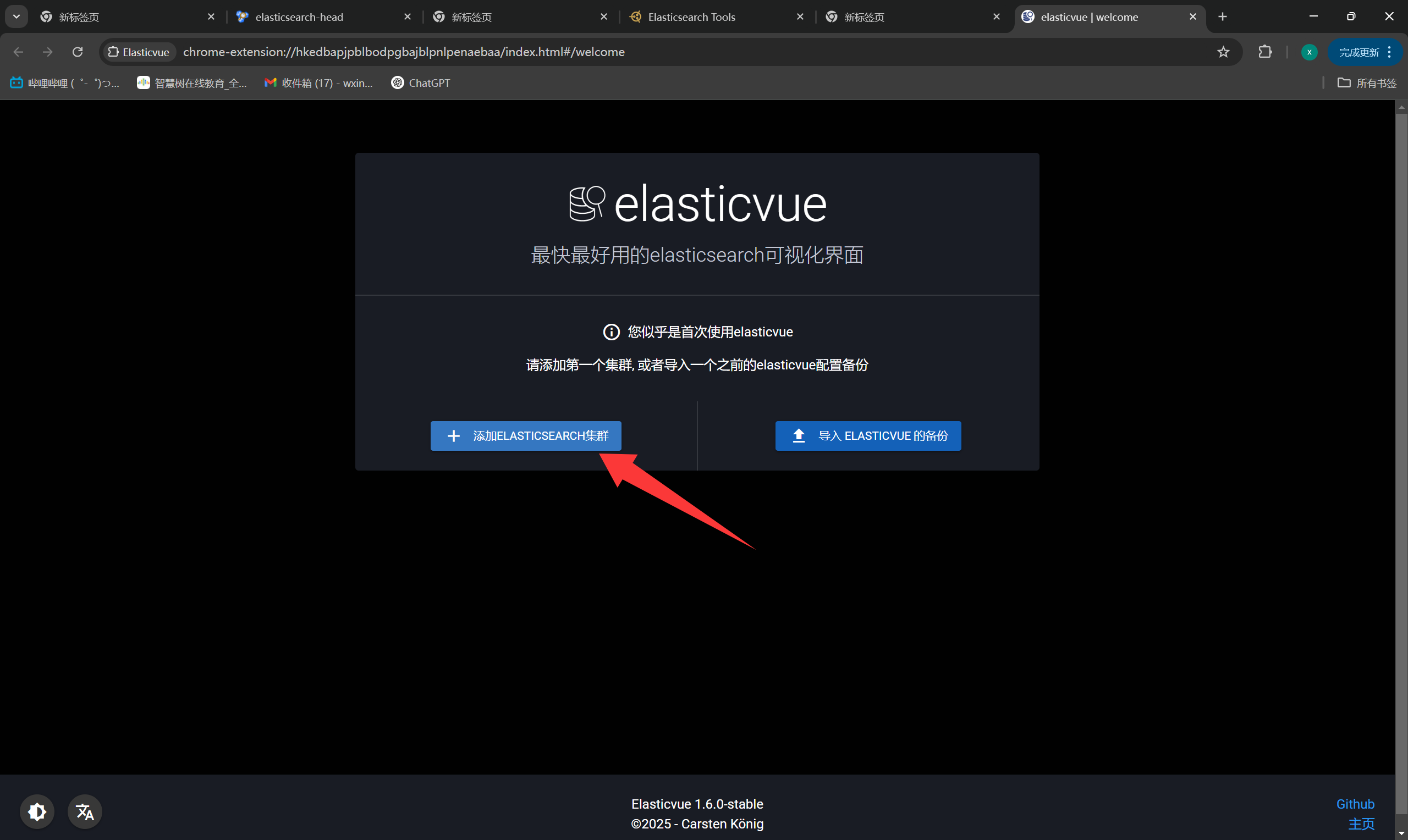
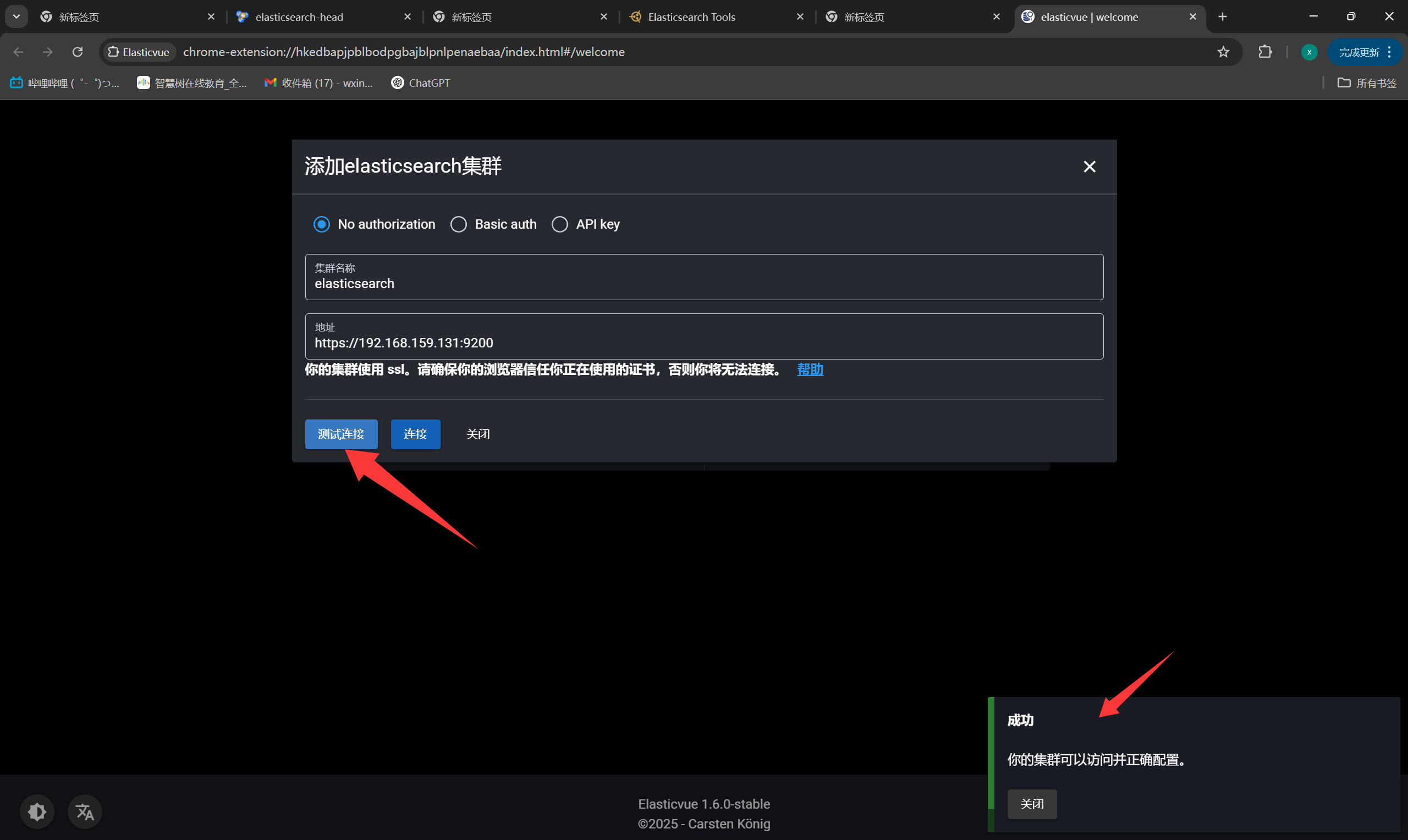
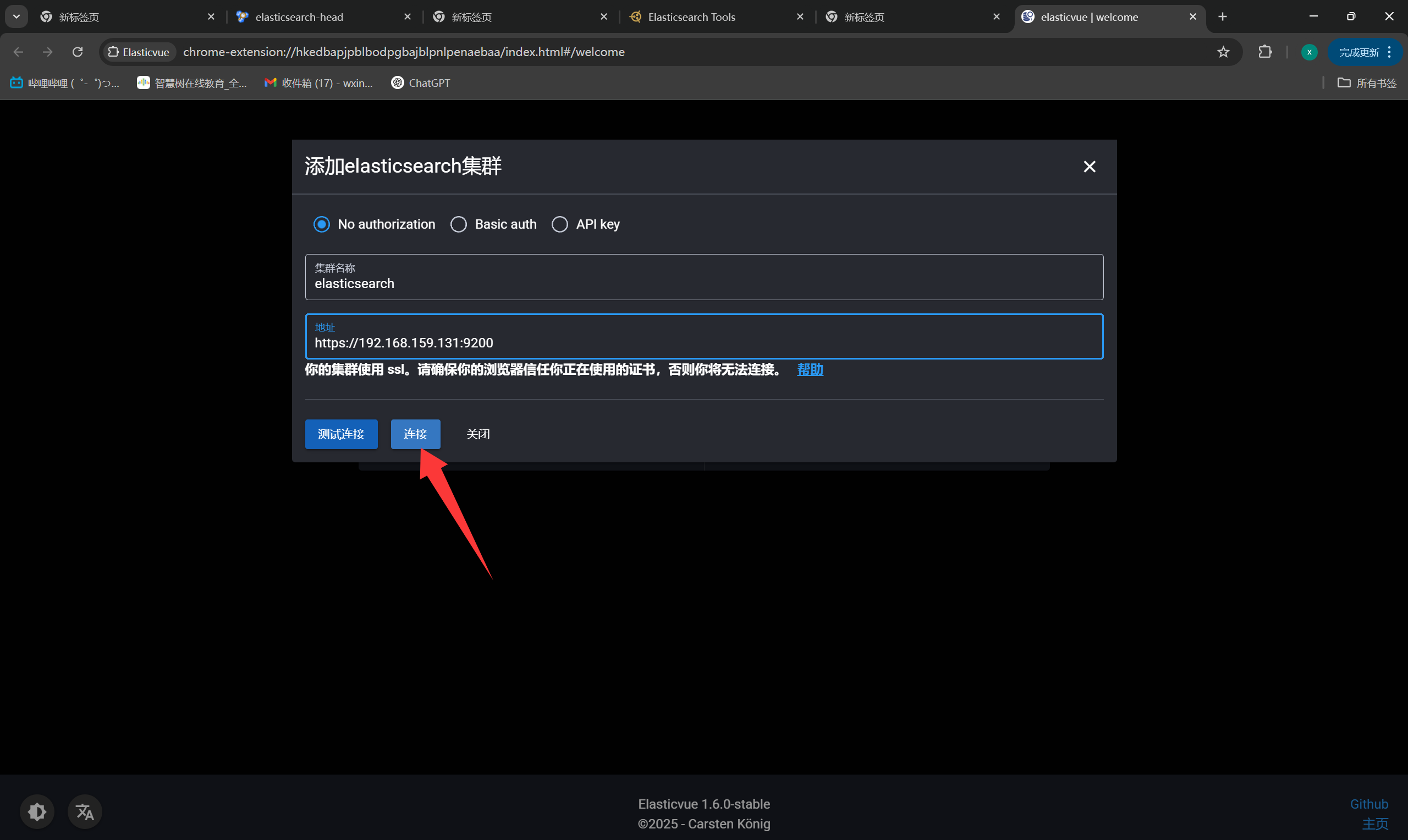
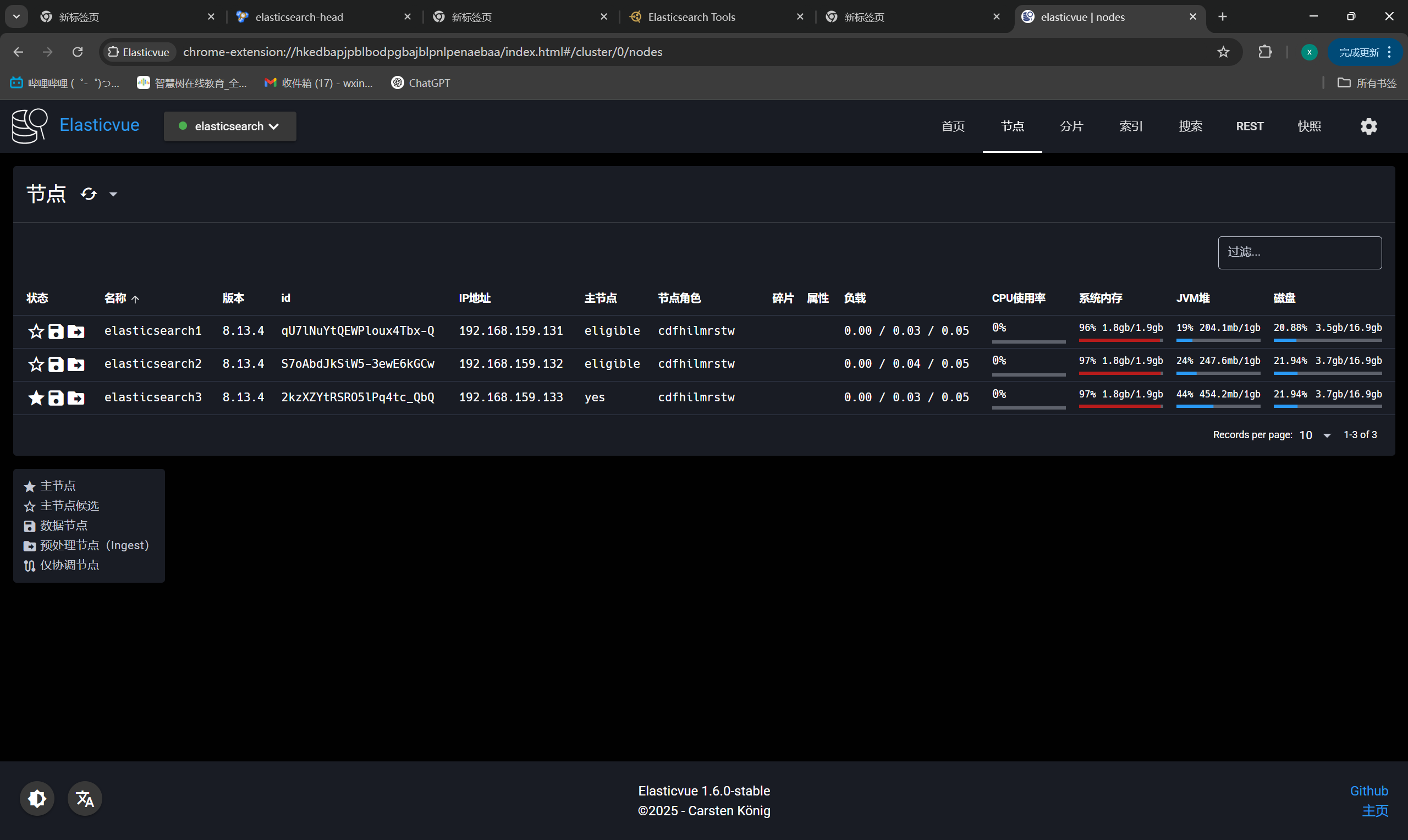
+Elasticvue
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## 四:基本概念
+
+### 1. elasticsearch 与传统数据的区别
+
+ 一个ES集群可以包含多个索引(数据库),每个索引又包含了很多类型(表),类型中包含了很多文档(行),每个文档使用 JSON 格式存储数据,包含了很多字段(列)。
+
+| 关系型数据库 | Elasticsearch |
+| :-------------: | :-----------------: |
+| 数据库>表>行>列 | 索引>类型>文档>字段 |
+
+### 2. 基本概念
+
+**索引(index)**
+
+ ES将数据存储于一个或多个索引中。类比传统的关系型数据库领域来说,索引相当于SQL中的一个数据库,索引由其名称(必须为全小写字符)进行标识。一个ES集群中可以按需创建任意数目的索引。
+
+**类型(type)**
+
+ 类型是索引内部的逻辑分区(category/partition),一个索引内部可定义一个或多个类型(type)。类比传统的关系型数据库领域来说,类型相当于“表”。
+
+**文档(document)**
+
+ 文档是索引和搜索的原子单位,它是包含了一个或多个域(Field)的容器,每个域拥有一个名字及一个或多个值,有多个值的域通常称为“多值域”,文档基于JSON格式进行表示。每个文档可以存储不同的域集,但同一类型下的文档至应该有某种程度上的相似之处。类比传统的关系型数据库领域来说,类型相当于“行”。
+
+**集群(cluster)**
+
+ 一个或者多个拥有相同cluster.name配置的节点组成, 它们共同承担数据和负载的压力。
+
+**节点(node)**
+
+ 一个运行中的 Elasticsearch 实例称为一个节点。es中的节点分为三种类型:
+
+- 主节点:负责管理集群范围内的所有变更,例如增加、删除索引,或者增加、删除节点等。 主节点并不需要涉及到文档级别的变更和搜索等操作。可以通过属性`node.master`进行设置。
+- 数据节点:存储数据和其对应的倒排索引。默认每一个节点都是数据节点(包括主节点),可以通过`node.data`属性进行设置。
+- 协调节点:如果`node.master`和`node.data`属性均为false,则此节点称为协调节点,用来响应客户请求,均衡每个节点的负载。
+
+注意:
+
+ 使用index和doc_type来组织数据。doc_type中的每条数据称为一个document,是一个JSON Object。
+
+ ES分布式搜索,传统数据库遍历式搜索
+
+**分片(Shards)**
+
+ 分片是Elasticsearch进行数据分布和扩展的基础。每个索引都可以被分割成多个分片,每个分片其实是一个独立的索引。分片使得Elasticsearch可以把巨大的数据集分散存储在多个节点上,这样可以实现:
+
+- 水平扩展:随着数据量的增加,可以通过增加更多的节点来分摊数据和负载,从而提高处理能力
+- 提升性能:搜索操作可以并行在多个分片上执行,每个分片处理的速度更快,整体搜索性能得以提升
+
+**副本(Replicas)**
+
+ 副本是分片的复制,主要用于提高数据的可用性和搜索查询的并发处理能力。每个分片都可以有一个或多个副本,这些副本分布在不同的节点上,从而提供了:
+
+- 数据可用性:当某个节点发生故障时,该节点上的分片如果有副本存在于其他节点上,那么这些副本可以保证数据不会丢失,并且服务还可以继续运行。
+- 负载均衡:读取操作(如搜索请求)可以在所有副本之间进行负载均衡,这样可以提高查询的吞吐量和响应速度。
+
+**定义分片和副本**
+
+ 创建索引时指定分片和副本数
+
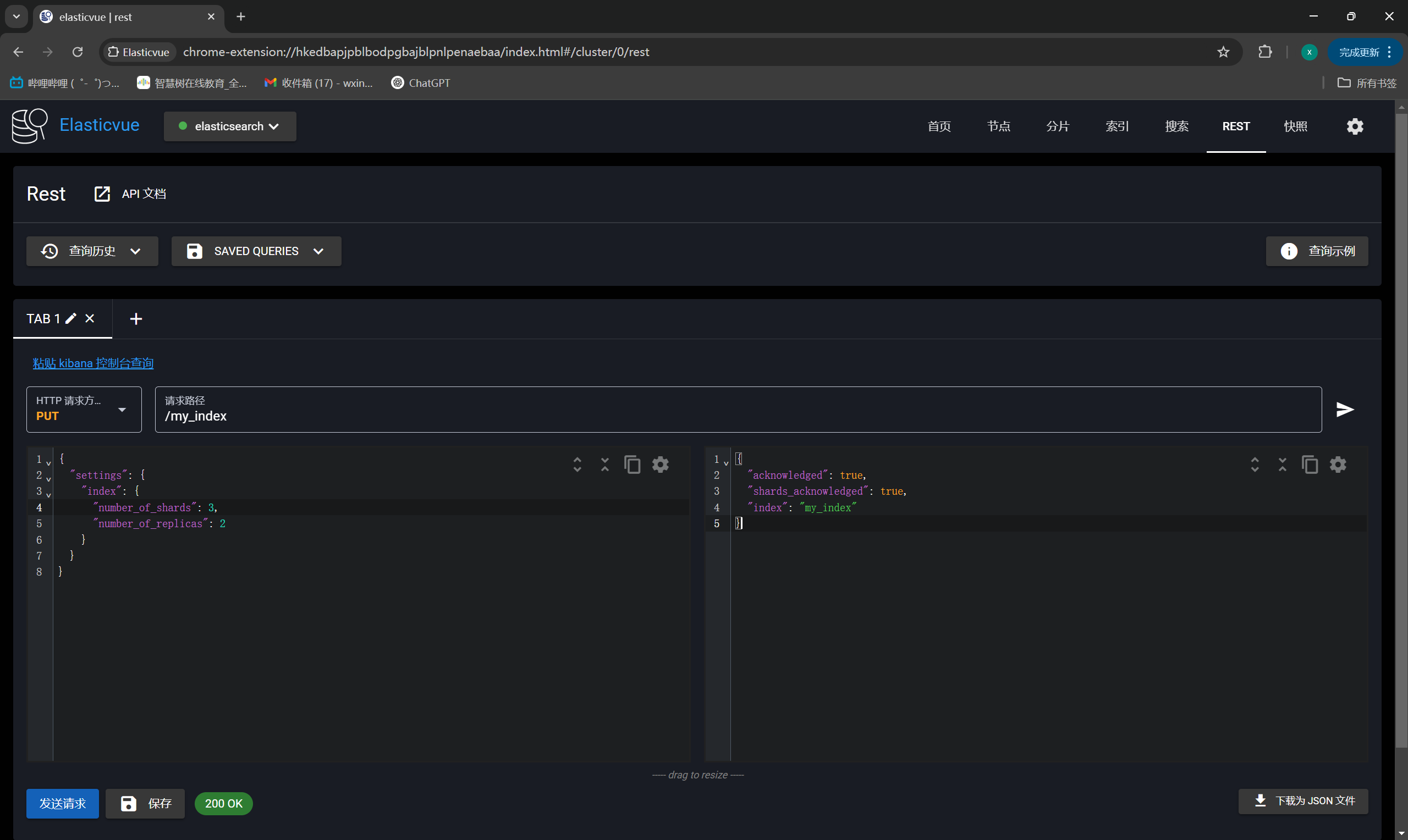
+ 当您通过Elasticsearch的REST API创建一个新的索引时,可以在请求体中使用settings部分来指定该索引的分片数(number_of_shards)和副本数(number_of_replicas)。以下是一个具体的示例:
+
+```json
+PUT /my_index
+{
+ "settings": {
+ "index": {
+ "number_of_shards": 3, # 指定该索引将有3个主分片
+ "number_of_replicas": 2 # 每个主分片将有2个副本分片
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+
+
+ 这个例子中,PUT /my_index是创建名为my_index的索引的请求。在请求体中,settings部分指出这个索引将被分成3个主分片,并且每个主分片将会有2个副本分片。这意味着,总共会有9个分片(3个主分片 + 6个副本分片)被分布在集群中。
+
+- 主分片数量:一旦索引被创建,其主分片的数量就无法更改。因此,在创建时应谨慎选择合适的分片数量。
+- 副本数量:与主分片数量不同,副本的数量是可以动态调整的。如果需要更多的数据冗余或查询吞吐量,可以增加副本的数量。
+- 伸缩性与性能:选择分片和副本的数量时需要考虑数据量、查询负载和集群的硬件资源。过多的分片可能会增加集群的管理开销,而过少的分片可能会限制数据和查询的伸缩性。
+
+分片数的确定
+
+- 数据量预估:估计索引的总数据量大小。一般来说,每个分片处理20GB到50GB数据是比较理想的。这不是固定规则,但可以作为一个起点。
+- 硬件资源:考虑你的硬件资源,尤其是内存和CPU。分片越多,消耗的资源也越多。确保你的Elasticsearch集群有足够的资源来处理这些分片。
+- 写入吞吐量:如果你的应用会有大量的写入操作,更多的分片可能有助于提高写入性能,因为可以并行写入多个分片。
+- 查询性能:更多的分片意味着查询可以并行于更多的分片上执行,这可能会提高查询性能。但是,如果每个查询都要访问大多数分片,那么管理过多的分片会减慢查询速度。
+
+副本数的确定
+
+- 数据可用性:至少有一个副本可以确保当某个节点失败时,数据不会丢失,并且Elasticsearch服务仍然可用。
+- 读取性能:更多的副本意味着更高的读取吞吐量,因为读取请求可以在多个副本之间分配。如果你的应用主要是读取密集型的,增加副本数可以提高查询性能。
+- 集群负载:考虑集群的整体负载。增加副本会提高数据冗余和读取性能,但也会增加存储需求和网络流量,因此需要确保你的硬件资源可以支持。
+
+## 五:Elasticsearch 集群架构
+
+### 1. Discovery 发现
+
+ 发现是集群形成模块寻找其他节点以形成集群的过程。当您启动 Elasticsearch 节点或节点认为主节点发生故障时,此过程将运行,并持续到找到主节点或选出新的主节点为止。
+
+ 此过程分为两个阶段:首先,每个节点通过连接到每个地址并尝试识别其所连接的节点以及验证其是否符合主节点资格来探测种子地址。其次,如果成功,它将与远程节点共享其所有已知符合主节点资格的对等节点的列表,然后远程节点依次与其对等节点进行响应。然后,节点探测它刚刚发现的所有新节点,请求其对等节点,依此类推。
+
+ 如果节点不符合主节点资格,则它将继续此发现过程,直到发现选举的主节点。如果没有发现选举的主节点,则节点将重试,之后`discovery.find_peers_interval`默认为`1s` 。
+
+ 如果节点符合主节点条件,则它会继续此发现过程,直到发现当选主节点或发现足够多的无主主节点来完成选举。如果上述两种情况都发生得不够快,则节点将重试,之后`discovery.find_peers_interval`默认为`1s`。
+
+ 一旦主节点被选出,它通常会继续担任主节点,直到被故意停止。如果 故障检测确定集群出现故障,它也可能会停止担任主节点。当某个节点不再是主节点时,它会再次开始发现过程。
+
+### 2. 种子主机提供商
+
+默认情况下,集群形成模块提供两个种子主机提供程序来配置种子节点列表
+
+- 基于设置的种子主机提供程序
+- 基于文件的种子主机提供程序
+
+ 种子主机提供程序使用设置进行配置`discovery.seed_providers` ,默认为基于设置的主机提供程序
+
+**基于设置的种子主机提供商:**
+
+ 基于设置的种子主机提供程序使用节点设置来配置种子节点地址的静态列表。这些地址可以作为主机名或 IP 地址指定;在每轮发现期间,指定为主机名的主机都会解析为 IP 地址。
+
+```yml
+discovery.seed_hosts:
+ - 192.168.159.131:9200
+ - 192.168.159.132:9200
+ - 192.168.159.133:9200
+
+或者:
+discovery.seed_hosts: ["192.168.159.131:9200","192.168.159.132:9200","192.168.159.133:9200"]
+```
+
+**基于文件的种子主机提供商:**
+
+ 基于文件的种子主机提供程序通过外部文件配置主机列表。Elasticsearch会在文件更改时重新加载此文件,这样种子节点列表就可以动态更改,而无需重新启动每个节点。例如,这为在Docker容器中运行的 Elasticsearch 实例提供了一种方便的机制,当节点启动时可能不知道这些IP地址时,可以动态地为其提供要连接的IP地址列表。
+
+```yaml
+discovery.seed_providers: file
+```
+
+ 然后按照下面描述的格式创建一个文件`$ES_PATH_CONF/unicast_hosts.txt`。每当对文件进行更改时,Elasticsearch都会获取新的更改并使用新的主机列表。
+
+ 该`unicast_hosts.txt`文件每行包含一个节点条目。每个节点条目由主机(主机名或 IP 地址)和一个可选的传输端口号组成。如果指定了端口号,它必须紧跟在主机之后(在同一行上)。
+
+ 允许使用主机名代替 IP 地址,并由 DNS 解析,如上所述。IPv6 地址必须在括号中给出,如果需要,端口号也应放在括号后面
+
+```bash
+cat $ES_PATH_CONF/unicast_hosts.txt
+10.10.10.5
+10.10.10.6:9305
+10.10.10.5:10005
+# an IPv6 address
+[2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334]:9301
+```
+
+### 3. 基于集群的决策
+
+ 选举主节点和更改集群状态是符合主节点条件的节点必须协同执行的两个基本任务。即使某些节点发生故障,这些活动也必须能够稳健地运行。Elasticsearch 通过在收到来自法定人数(集群中符合主节点条件的节点的子集)的响应后将每个操作视为成功来实现这种稳健性。仅要求一部分节点响应的优点是,这意味着某些节点可以发生故障而不会阻止集群继续运行。法定人数是经过精心选择的,即集群被分成两部分,以至于每个部分可能做出与另一部分不一致的决策。
+
+ Elasticsearch 允许您向正在运行的集群添加和删除符合主节点条件的节点。在许多情况下,您只需根据需要启动或停止节点即可完成此操作。
+
+ 随着节点的添加或删除,Elasticsearch 通过更新集群的**投票配置**来保持最佳容错水平,投票配置是一组符合主节点条件的节点,在做出诸如选举新主节点或提交新集群状态等决策时,这些节点的响应会被计算在内。只有在投票配置中超过一半的节点做出响应后,才会做出决策。通常,投票配置与集群中当前所有符合主节点条件的节点集相同。但是,在某些情况下,它们可能会有所不同。
+
+ 为了确保集群保持可用,不能同时停止投票配置中的一半或更多节点。只要超过一半的投票节点可用,集群仍可正常工作。这意味着,如果有三个或四个主节点,集群可以容忍其中一个不可用。如果有两个或更少的主节点,它们必须全部保持可用。
+
+ 如果您同时停止投票配置中的一半或更多节点,则集群将不可用,直到您使足够多的节点重新联机以再次形成法定人数。当集群不可用时,任何剩余节点都会在其日志中报告它们无法发现或选举主节点。
+
+### 4. 主节点选举
+
+ Elasticsearch使用选举流程来商定选举的主节点,无论是在启动时还是在现有选举主节点发生故障时。任何符合主节点条件的节点都可以启动选举,通常第一次选举将会成功。只有当两个节点恰好同时开始选举时,选举才会失败,因此每个节点都会随机安排选举以降低发生这种情况的概率。节点将重试选举,直到选出主节点,如果失败则放弃,以便最终选举能够成功(概率任意高)。主节点选举的安排由主节点选举设置控制。
+
+### 5. 投票配置
+
+ 每个 Elasticsearch 集群都有一个投票配置,它是一组 符合主节点条件的节点,在做出诸如选举新主节点或提交新集群状态等决策时,这些节点的响应会被计入。只有在投票配置中的大多数节点(超过一半)响应后,才会做出决策。通常,投票配置与集群中当前所有符合主节点条件的节点集相同。但是,在某些情况下,它们可能会有所不同。
+
+ 较大的投票配置通常更具弹性,因此 Elasticsearch 通常倾向于在符合主节点资格的节点加入集群后将其添加到投票配置中。同样,如果投票配置中的节点离开集群,并且集群中还有另一个不符合主节点资格的节点不在投票配置中,则最好交换这两个节点。因此,投票配置的大小保持不变,但其弹性会增加。
+
+ 在节点离开集群后自动从投票配置中删除节点并不是那么简单。不同的策略有不同的优点和缺点,可以使用设置来控制投票配置是否自动`cluster.auto_shrink_voting_configuration`
+
+ 如果`cluster.auto_shrink_voting_configuration`设置为`true`(这是默认值和推荐值)并且集群中至少有三个主合格节点,则只要除一个主合格节点之外的所有节点都健康,Elasticsearch 仍然能够处理集群状态更新
+
+ 在某些情况下,Elasticsearch 可能会容忍多个节点丢失,但这并不能保证在所有故障序列下都能做到。如果设置`cluster.auto_shrink_voting_configuration`为`false`,则必须手动从投票配置中移除已离开的节点。
+
+配置参数如下:
+
+```
+cluster.auto_shrink_voting_configuration
+(动态)控制投票配置是否自动删除已离开的节点(只要它仍包含至少 3 个节点)。默认值为true。如果设置为,投票配置永远不会自动缩小,您必须使用投票配置排除 APIfalse手动删除已离开的节点 。
+
+cluster.election.back_off_time
+(静态)设置每次选举失败时选举前等待时间的上限增加量。请注意,这是线性退避。默认值为 100ms。更改此设置(默认设置)可能会导致您的集群无法选举主节点。
+
+cluster.election.duration
+(静态)设置每次选举允许花费多长时间,之后节点才会认为选举失败并安排重试。默认值为500ms。更改此设置可能会导致您的集群无法选举出主节点。
+
+cluster.election.initial_timeout
+(静态)设置节点在首次尝试选举之前(或当选主节点失败后)等待的时间上限。默认值为 100ms。更改此设置(默认设置)可能会导致您的集群无法选举主节点。
+
+cluster.election.max_timeout
+(静态)设置节点在尝试首次选举之前等待时间的最大上限,以便长时间持续的网络分区不会导致选举过于稀疏。默认值为10s。更改此设置(默认设置)可能会导致您的集群无法选举主节点。
+
+cluster.fault_detection.follower_check.interval
+(静态)设置当选主节点在集群中每个其他节点的跟随节点检查之间等待的时间。默认为1s。更改此设置(默认设置除外)可能会导致集群变得不稳定。
+
+cluster.fault_detection.follower_check.timeout
+(静态)设置当选主节点等待跟随者检查响应的时间,超过该时间则认为主节点失败。默认为10s。更改此设置可能会导致集群变得不稳定。
+
+cluster.fault_detection.follower_check.retry_count
+(静态)设置每个节点必须发生多少次连续的跟随者检查失败,当选主节点才会认为该节点有故障并将其从集群中移除。默认为3。更改此设置可能会导致集群变得不稳定。
+
+cluster.fault_detection.leader_check.interval
+(静态)设置每个节点在检查当选主节点之间等待的时间。默认为 1s。更改此设置可能会导致集群变得不稳定。
+
+cluster.fault_detection.leader_check.timeout
+(静态)设置每个节点等待当选主节点对领导者检查的响应的时间,超过该时间则认为主节点已发生故障。默认为10s。更改此设置可能会导致集群变得不稳定。
+
+cluster.fault_detection.leader_check.retry_count
+(静态)设置必须发生多少次连续的领导者检查失败,节点才会认为当选主节点有故障,并尝试查找或选举新主节点。默认为3。更改此设置(默认设置)可能会导致集群变得不稳定。
+
+cluster.follower_lag.timeout
+(静态)设置主节点等待从滞后节点接收集群状态更新确认的时间。默认值为90s。如果节点在此时间段内未成功应用集群状态更新,则该节点被视为发生故障并从集群中删除。请参阅 发布集群状态。
+
+cluster.max_voting_config_exclusions
+(动态)设置一次投票配置排除的数量限制。默认值为10。请参阅在集群中添加和删除节点。
+
+cluster.publish.info_timeout
+(静态)设置主节点等待每个集群状态更新完全发布到所有节点的时间,然后记录一条消息,表明某些节点响应缓慢。默认值为10s。
+
+cluster.publish.timeout
+(静态)设置主节点等待每个集群状态更新完全发布到所有节点的时间,除非discovery.type设置为 single-node。默认值为30s。请参阅发布集群状态。
+
+cluster.discovery_configuration_check.interval
+(静态)设置某些检查的间隔,这些检查将记录有关不正确的发现配置的警告。默认值为30s。
+
+cluster.join_validation.cache_timeout
+(静态)当一个节点请求加入集群时,当选的主节点会向其发送一份最新集群状态的副本,以检测可能阻止新节点加入集群的某些问题。主节点会缓存其发送的状态,如果另一个节点不久后加入集群,则使用缓存的状态。此设置控制主节点等待清除此缓存的时间。默认为60s。
+```
+
+ 通常,集群中的主节点数应为奇数。如果为偶数,Elasticsearch 会将其中一个节点排除在投票配置之外,以确保其大小为奇数
+
+### 6. 引导集群
+
+ 首次启动 Elasticsearch 集群时,需要在集群中的一个或多个主节点上明确定义初始主节点集。这称为集群引导。这仅在集群首次启动时才需要。加入正在运行的集群的新启动节点从集群的选定主节点获取此信息。
+
+ `cluster.initial_master_nodes`初始的符合主节点资格的节点集在设置中定义 。这应该设置为一个列表,其中包含每个符合主节点资格的以下项目之一:
+
+- 节点名称
+- node.name如果未设置,则默认为节点的主机名
+
+ 集群形成后,`cluster.initial_master_nodes`从每个节点的配置中删除该设置。不应为非主节点、加入现有集群的主节点或正在重新启动的节点设置该设置。
+
+**配置使用如下:**
+
+ 创建新集群的最简单方法是选择一个主节点,该节点将自行引导到单节点集群中,然后所有其他节点将加入该集群。
+
+```yaml
+cluster.initial_master_nodes: elasticsearch1
+```
+
+ 对于容错集群引导,请使用所有符合主节点条件的节点。例如,如果您的集群有 3 个符合主节点条件的节点,节点名称`elasticsearch1`为,`elasticsearch2`则按`elasticsearch3`如下方式配置它们:
+
+```yaml
+cluster.initial_master_nodes:
+ - elasticsearch1
+ - elasticsearch2
+ - elasticsearch3
+```
+
+**选择集群名称:**
+
+ 此`cluster.name`设置允许您创建多个彼此独立的集群。节点在首次连接时会验证它们是否同意其集群名称,并且 Elasticsearch 只会从具有相同集群名称的节点组成集群。集群名称的默认值为elasticsearch,但建议将其更改为反映集群的逻辑名称。
+
+**开发模式下的自动引导:**
+
+ 默认情况下,每个节点在首次启动时都会自动引导到单节点集群。如果配置了以下任何设置,则不会进行自动引导:
+
+```
+discovery.seed_providers
+discovery.seed_hosts
+cluster.initial_master_nodes
+```
+
+注意:
+
+ 一旦 Elasticsearch 节点加入现有集群或引导新集群,它就不会再加入其他集群。Elasticsearch 不会在集群形成后将单独的集群合并在一起,即使您随后尝试将所有节点配置为单个集群。这是因为没有办法将这些单独的集群合并在一起而不丢失数据。
+
+## 六:IK 分词器
+
+### 1. 简介
+
+ ES IK分词器是一种基于中文文本的分词器,它是Elasticsearch中文分词的一种实现。它采用了自然语言处理技术,可以将中文文本进行切分,抽取出其中的词汇,从而提高搜索引擎对中文文本的搜索和检索效率。
+
+ ES IK分词器的原理是采用了一种叫做“正向最大匹配”(Forward Maximum Matching,简称FMM)和“逆向最大匹配”(Backward Maximum Matching,简称BMM)的分词算法,通过对文本进行多次切分,最终确定最优的分词结果。
+
+ ES IK分词器可以用于各种中文文本处理应用,包括搜索引擎、文本挖掘、信息检索等。它支持多种分词模式,包括最细粒度切分、智能切分和最大切分等模式,可以根据具体应用场景进行灵活配置。
+
+### 2. 分类
+
+**细粒度分词模式(ik_max_word):**
+
+- 在这种模式下,IK分词器会尽可能地按照词典中的词语进行最大长度匹配,将文本切分成连续的词语序列
+- 这种模式适用于对文本进行细致的切分,尽可能将句子切分为最小的词语单元,获得更加精确的分词结果
+
+**智能分词模式(ik_smart):**
+
+- 在智能切分模式下,IK分词器会结合词典匹配和机器学习算法,根据上下文信息分词,保留词语的完整性
+- 这种模式能够更好地处理一些特殊情况,如未登录词和新词等,提高了分词的准确性和适用性
+
+### 3. 下载地址
+
+https://github.com/infinilabs/analysis-ik/releases/tag/Latest
+
+### 4. 安装插件
+
+注意:
+
+- 安装的插件版本需要跟elasticsearch的版本一致,否则无法安装或报错
+- 安装完成后重启elasticsearch
+
+```bash
+[elasticsearch@elasticsearch1 ~]$ /usr/local/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-plugin install https://get.infini.cloud/elasticsearch/analysis-ik/8.13.4
+warning: ignoring JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/elasticsearch/jdk; using bundled JDK
+-> Installing https://get.infini.cloud/elasticsearch/analysis-ik/8.13.4
+-> Downloading https://get.infini.cloud/elasticsearch/analysis-ik/8.13.4
+@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@
+@ WARNING: plugin requires additional permissions @
+@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@
+* java.net.SocketPermission * connect,resolve
+See https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/technotes/guides/security/permissions.html
+for descriptions of what these permissions allow and the associated risks.
+
+Continue with installation? [y/N]y
+-> Installed analysis-ik
+```
+
+### 5. 项目需求
+
+如果对应的项目使用到了ES IK插件,我们需要在ES集群中构建IK环境
+
+## 七:冷热温节点部署
+
+### 1. 简介
+
+ 在某些大规模数据分析场景(比如时间数据分析),可以采用此架构:基于时间创建 index,然后持续地把温/冷数据迁移到相应的数据节点。
+
+ 专有主节点:由于不保存数据,也就不参与索引和查询操作,不会被长 GC 干扰,负载可以保持在较低水平,能极大提高集群的稳定性
+
+ 热数据节点:保存近期的 index,承担最频繁的写入和查询操作,可以配置较高的资源,如超高性能主机及硬盘。可以在集群配置参数里 Elasticsearch 节点的参数`node.attr.data`(热)做修改,默认为 `hot`
+
+ 温/冷数据节点:保存只读 index,会接收少量的查询请求,可以配置较低的资源。可以在集群配置参数里 Elasticsearch 节点的参数 `node.attr.data`(温)和` node.attr.data`(冷)做修改,默认为 `warm`和` cold`
+
+### 2. 准备工作
+
+前期部署参考:三:集群部署
+
+### 3. 修改配置
+
+es-1-data_hot
+
+```bash
+[elasticsearch@elasticsearch1 ~]$ vim /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/elasticsearch.yml
+cluster.name: elasticsearch
+node.name: elasticsearch1
+path.data: /usr/local/elasticsearch/data
+path.logs: /usr/local/elasticsearch/logs
+network.host: 0.0.0.0
+http.port: 9200
+node.roles: [data_hot,data_content,master,ingest]
+discovery.seed_hosts: ["192.168.159.131:9200", "192.168.159.132:9200","192.168.159.133:9200"]
+cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["elasticsearch1"]
+xpack.security.enabled: true
+xpack.security.enrollment.enabled: true
+xpack.security.http.ssl:
+ enabled: true
+ keystore.path: /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs/http.p12
+ truststore.path: /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs/http.p12
+xpack.security.transport.ssl:
+ enabled: true
+ verification_mode: certificate
+ keystore.path: /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs/elastic-certificates.p12
+ truststore.path: /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs/elastic-certificates.p12
+http.host: [_local_, _site_]
+ingest.geoip.downloader.enabled: false
+xpack.security.http.ssl.client_authentication: none
+http.cors.enabled: true
+http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
+```
+
+es-2-data_warm
+
+```bash
+[elasticsearch@elasticsearch2 ~]$ vim /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/elasticsearch.yml
+cluster.name: elasticsearch
+node.name: elasticsearch2
+path.data: /usr/local/elasticsearch/data
+path.logs: /usr/local/elasticsearch/logs
+network.host: 0.0.0.0
+http.port: 9200
+node.roles: [data_warm, data_content, master, ingest]
+discovery.seed_hosts: ["192.168.159.131:9200", "192.168.159.132:9200","192.168.159.133:9200"]
+cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["elasticsearch1"]
+xpack.security.enabled: true
+xpack.security.enrollment.enabled: true
+xpack.security.http.ssl:
+ enabled: true
+ keystore.path: /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs/http.p12
+ truststore.path: /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs/http.p12
+xpack.security.transport.ssl:
+ enabled: true
+ verification_mode: certificate
+ keystore.path: /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs/elastic-certificates.p12
+ truststore.path: /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs/elastic-certificates.p12
+http.host: [_local_, _site_]
+ingest.geoip.downloader.enabled: false
+xpack.security.http.ssl.client_authentication: none
+http.cors.enabled: true
+http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
+```
+
+es-3-data_cold
+
+```bash
+cluster.name: elasticsearch
+node.name: elasticsearch3
+path.data: /usr/local/elasticsearch/data
+path.logs: /usr/local/elasticsearch/logs
+network.host: 0.0.0.0
+http.port: 9200
+node.roles: [data_cold, data_content, master, ingest]
+discovery.seed_hosts: ["elasticsearch1", "elasticsearch2","elasticsearch3"]
+cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["elasticsearch1"]
+xpack.security.enabled: true
+xpack.security.enrollment.enabled: true
+xpack.security.http.ssl:
+ enabled: true
+ keystore.path: /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs/http.p12
+ truststore.path: /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs/http.p12
+xpack.security.transport.ssl:
+ enabled: true
+ verification_mode: certificate
+ keystore.path: /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs/elastic-certificates.p12
+ truststore.path: /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs/elastic-certificates.p12
+http.host: [_local_, _site_]
+ingest.geoip.downloader.enabled: false
+xpack.security.http.ssl.client_authentication: none
+http.cors.enabled: true
+http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
+```
+
+### 4. 启动服务
+
+依次启动所有节点
+
+```bash
+[elasticsearch@elasticsearch1 ~]$ nohup /usr/local/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch &
+[elasticsearch@elasticsearch2 ~]$ nohup /usr/local/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch &
+[elasticsearch@elasticsearch3 ~]$ nohup /usr/local/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch &
+```
+
+### 5. 修改密码
+
+依次修改所有节点
+
+```bash
+[elasticsearch@elasticsearch1 ~]$ /usr/local/es/bin/elasticsearch-reset-password -u elastic -i
+warning: ignoring JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/es/jdk; using bundled JDK
+This tool will reset the password of the [elastic] user.
+You will be prompted to enter the password.
+Please confirm that you would like to continue [y/N]y
+
+
+Enter password for [elastic]:
+Re-enter password for [elastic]:
+Password for the [elastic] user successfully reset.
+```
+
+### 6. 访问验证
+
+```
+GET /_cat/nodes
+```
+
+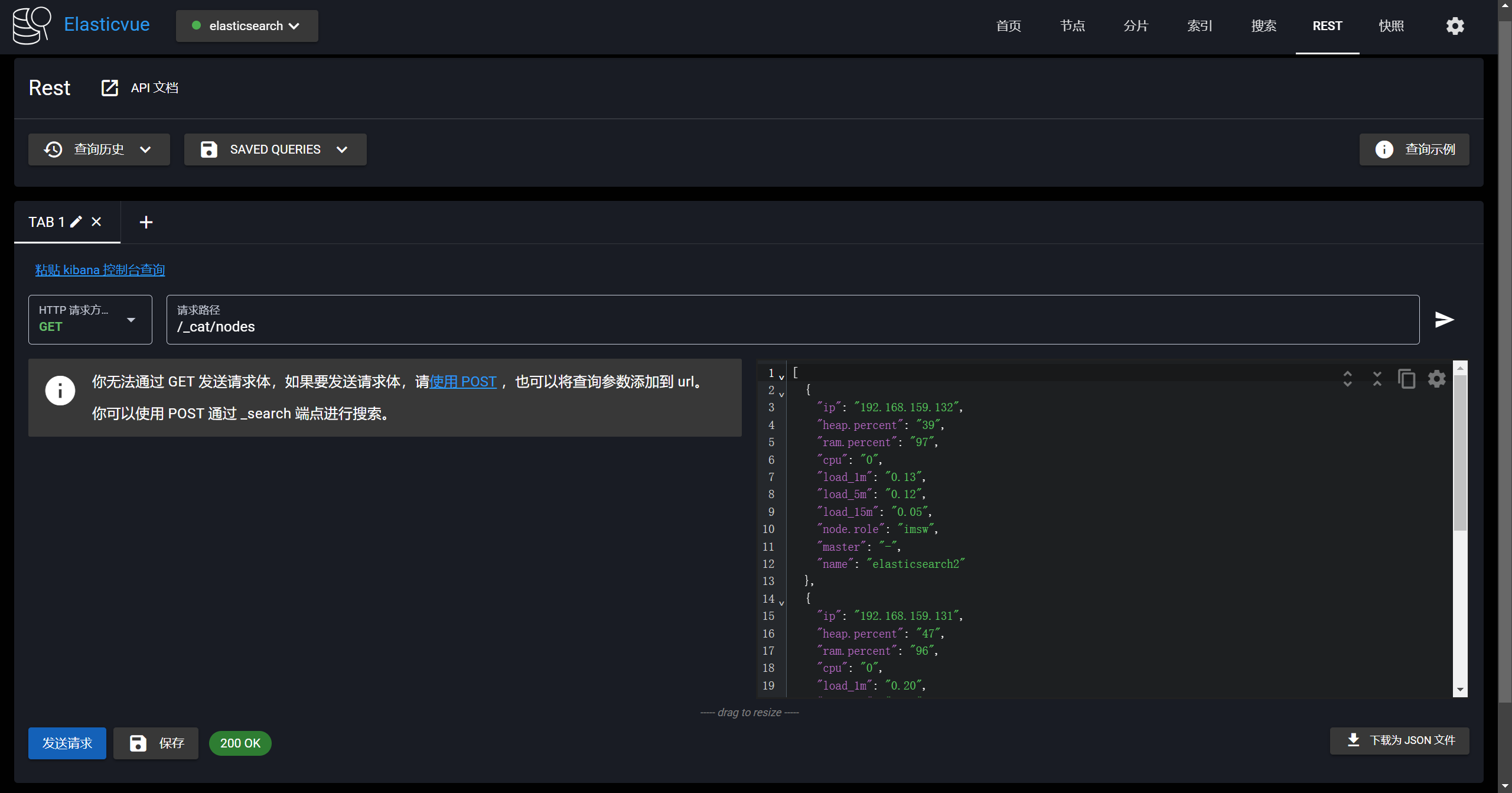
+
+### 7. 应用案例
+
+设置特定的索引,分片设置为5
+
+```yaml
+PUT kibana_sample_data_logs_ext
+{
+ "settings": {
+ "number_of_replicas": 0,
+ "number_of_shards": 5
+ }
+}
+```
+
+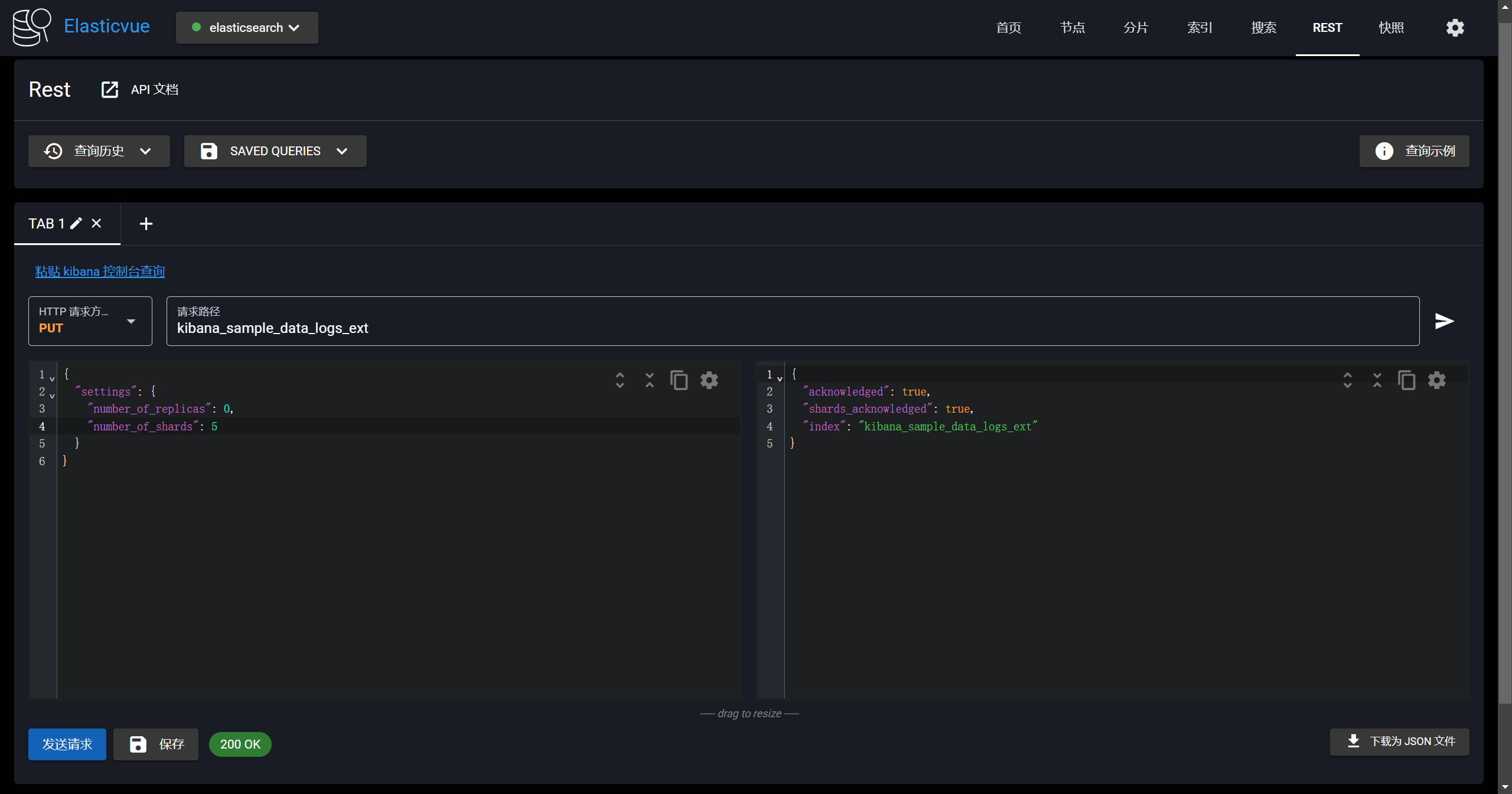
+
+准备索引数据,首先你得先确保您索引有:wxin
+
+```yaml
+POST _reindex
+{
+ "source": {
+ "index": "wxin"
+ },
+ "dest": {
+ "index": "kibana_sample_data_logs_ext"
+ }
+}
+```
+
+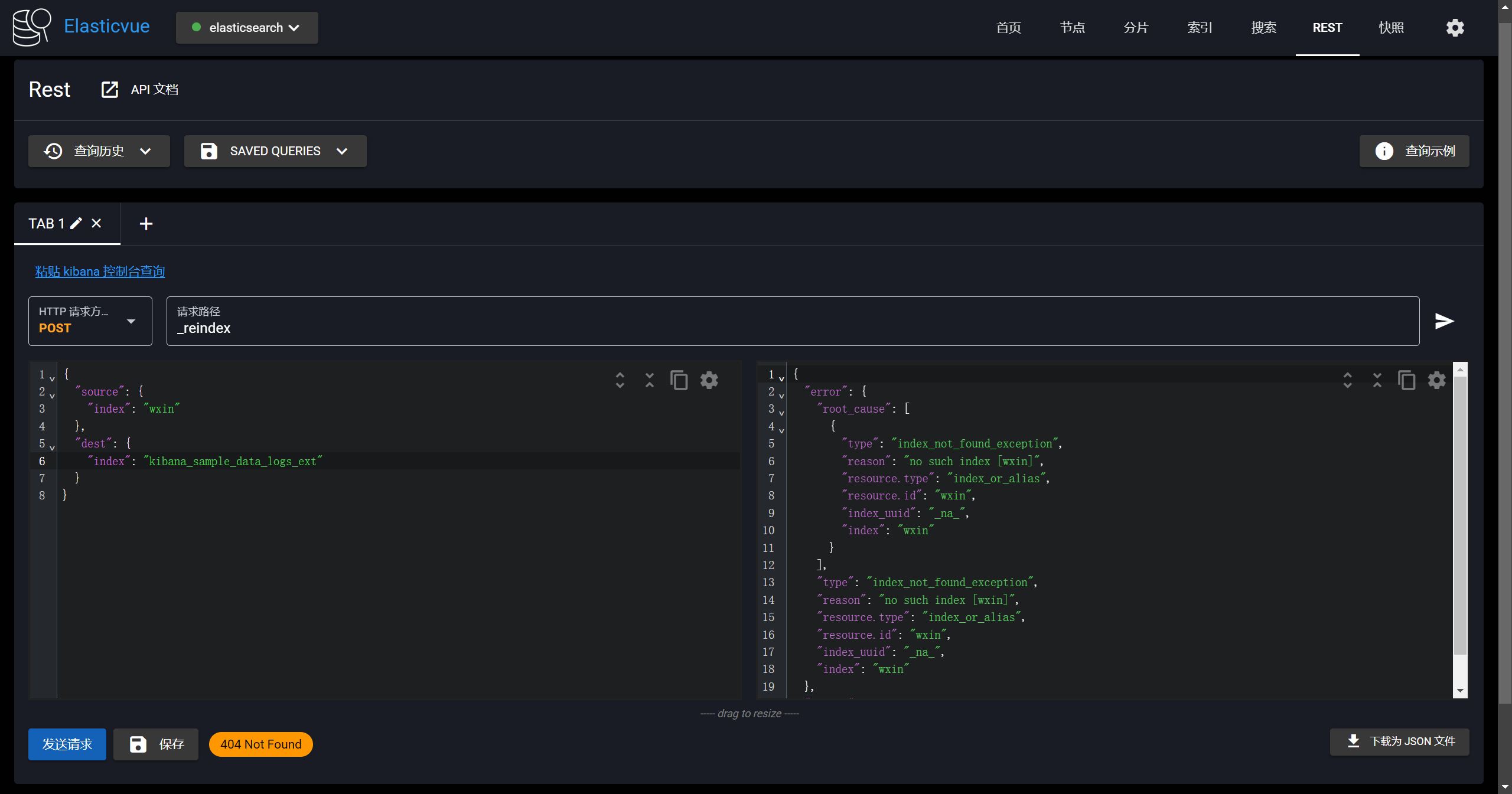
+
+这是现在的分片情况
+
+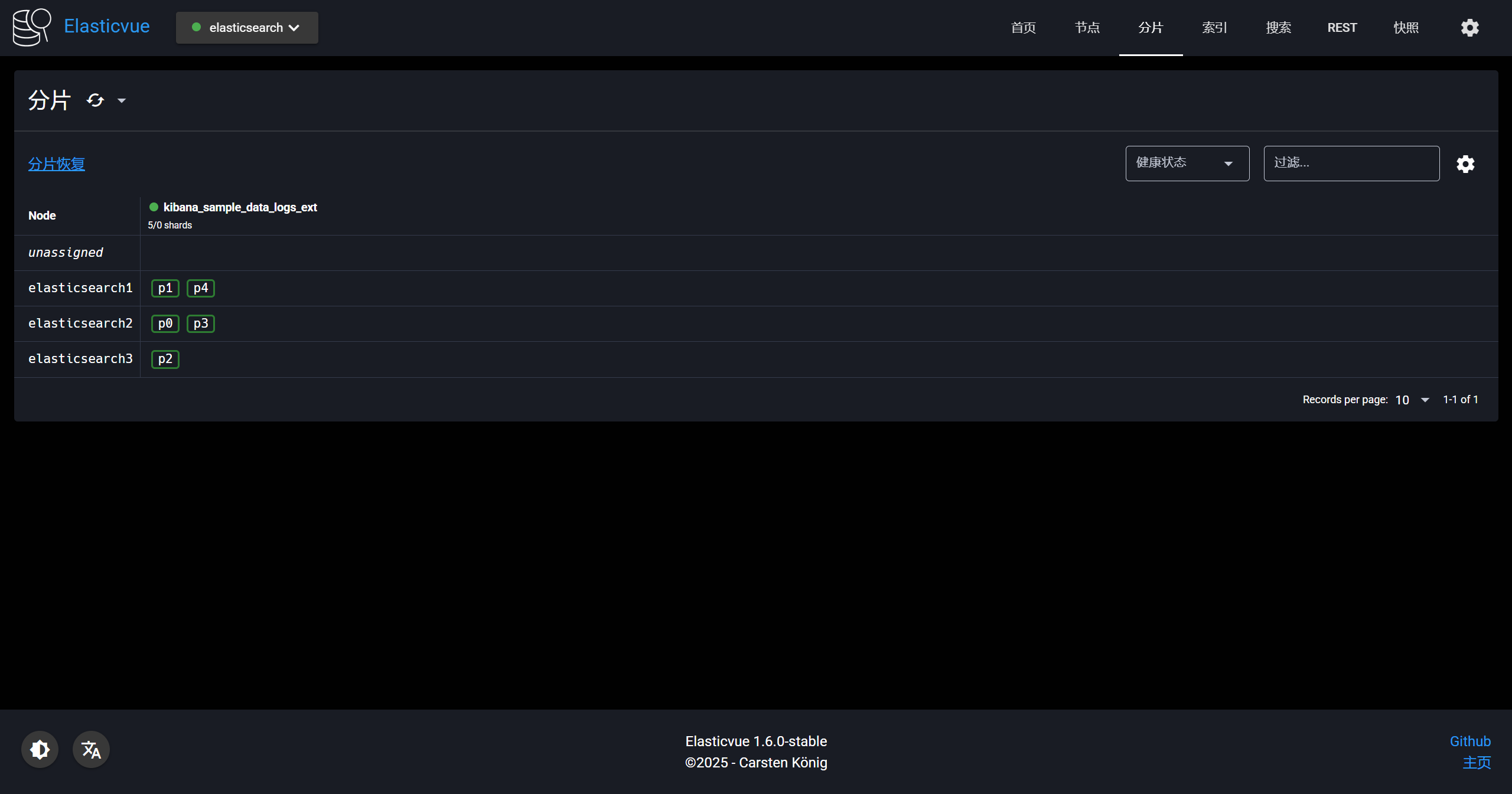
+
+设置索引分片信息,主要参数:index.routing.allocation.include._tier_preference
+
+索引-路由-分配,分配到data_hot节点上,之前我们在配置文件内定义的节点
+
+```yaml
+PUT kibana_sample_data_logs_ext/_settings
+{
+ "settings": {
+ "index.number_of_replicas": 0,
+ "index.routing.allocation.include._tier_preference": "data_hot",
+ "index.blocks.write": true
+ }
+}
+```
+
+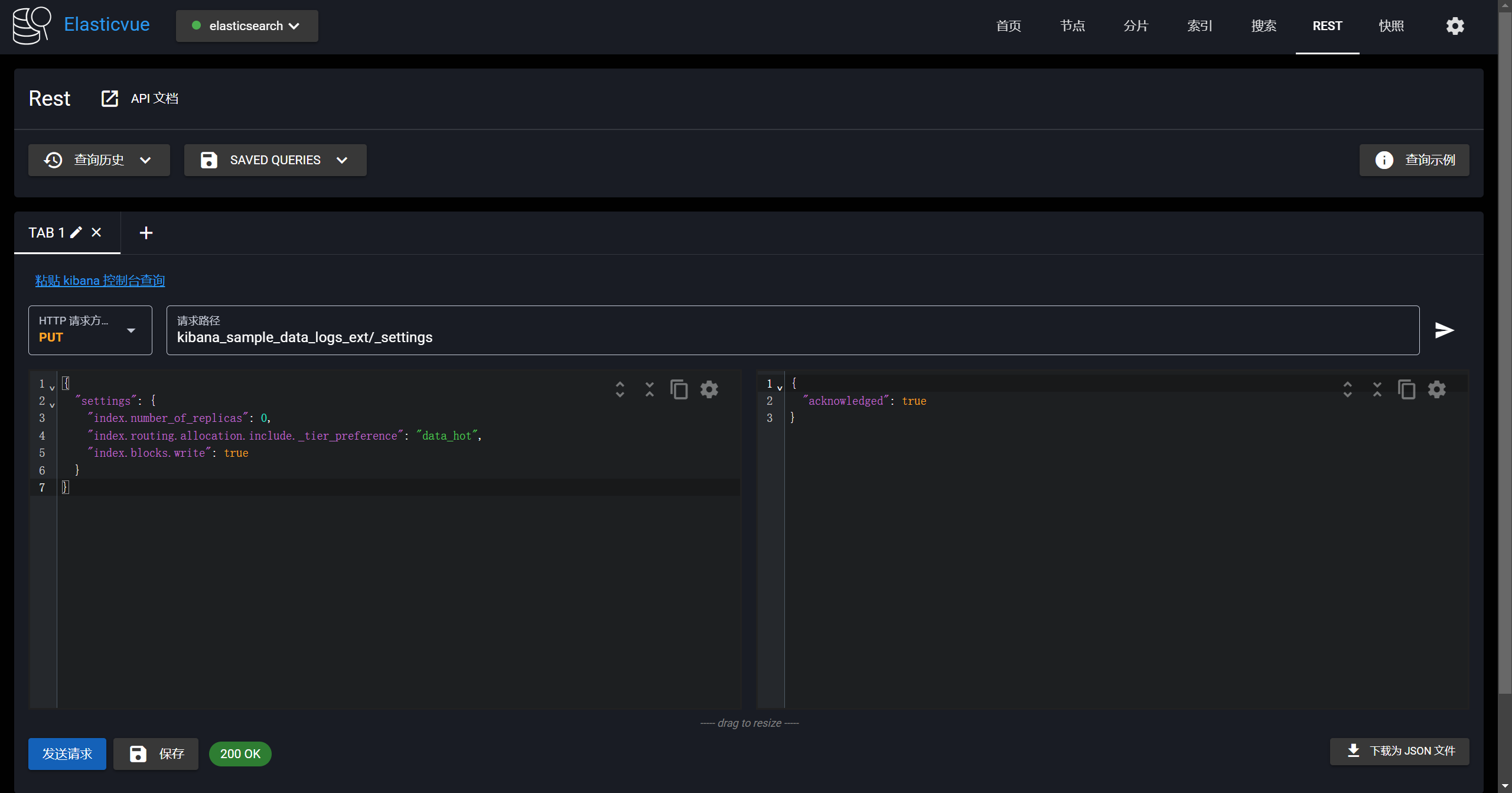
+
+在查询就能看到分片都在hot节点上了
+
+