33 KiB
Ansible 自动化运维
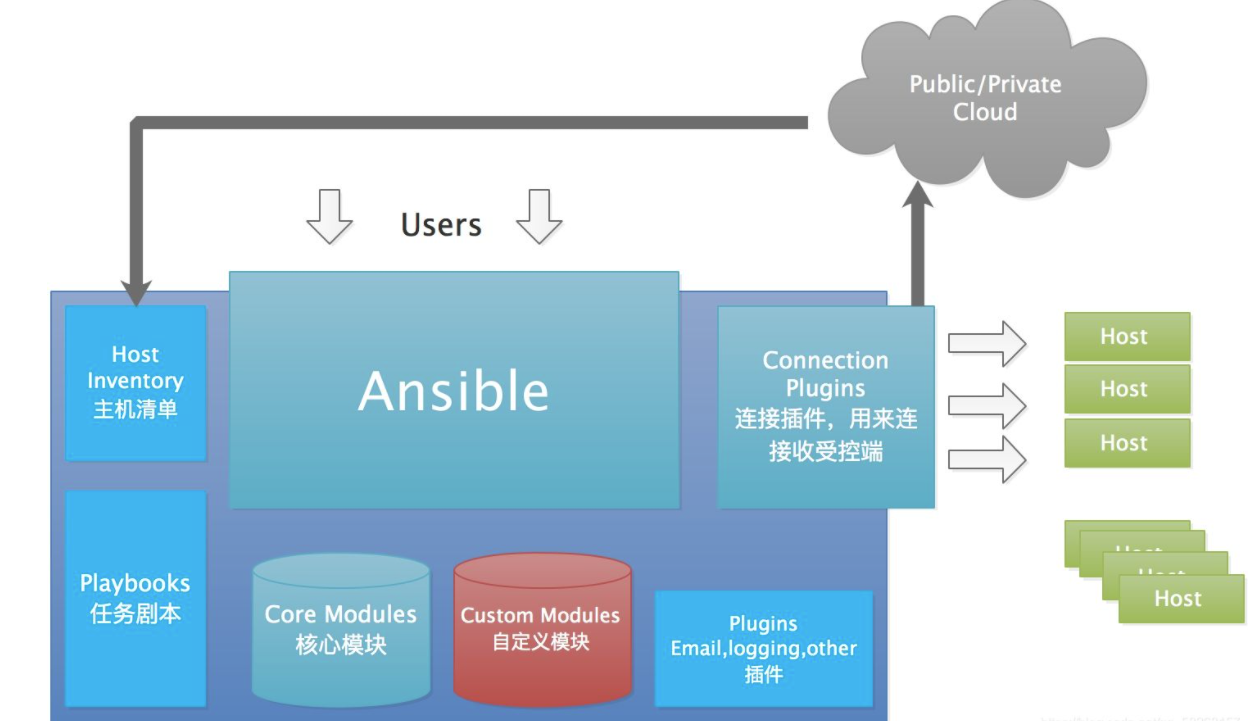
一:简介
1. 几种常用运维工具比较
Puppet:基于 Ruby 开发,采用 C/S 架构,扩展性强,基于 SSL,远程命令执行相对较弱。
SaltStack:基于 Python 开发,采用 C/S 架构,YAML 使得配置脚本更简单。需要配置客户端及服务器;每台被控制节点需要安装 agent。
Ansible:基于 Python 开发,分布式,无需客户端,轻量级,配置语法使用 YAML 语言,更强的远程命令执行操作。
2. Ansible 简介
Ansible 基于 Python 开发,集合了众多运维工具(puppet、cfengine、chef、func、fabric)的优点,实现了批量系统配置、批量程序部署、批量运行命令等功能。ansible 是基于模块工作的,本身没有批量部署的能力。真正具有批量部署的是 ansible 所运行的模块,ansible 只是提供一种框架。
- connection plugins:连接插件,负责和被监控端实现通信,有SSH,ZEROMQ等,默认使用SSH连接。
- host inventory:主机清单,是一个配置文件里面定义监控的主机。
- modules:模块,核心模块、command模块、自定义模块等。
- plugins:modules功能的补充,包括链接插件,邮件插件等。
- playbook:编排,定义Ansible多任务配置文件,非必须。
3. Ansible 特性
- no agents:不需要在被管控主机上安装任何客户端,更新时,只需在操作机上进行一次更新即可。
- no server:无服务端,使用时直接运行命令即可。
- modules in any languages:基于模块工作,可使用任意语言开发模块。
- yaml,not code:使用yaml语言定制剧本playbook。
- ssh by default:基于SSH工作。
- strong multi-tier solution:可实现多级指挥。
4. 部署 Ansible
环境准备:
环境
主机:4台 一个控制节点 三个被控制节点
解析:本地互相解析
# vim /etc/hosts
192.168.159.130 ansible-server
192.168.159.131 ansible-web1
192.168.159.132 ansible-web2
192.168.159.133 ansible-web3
配置ssh公钥认证:控制节点需要发送ssh公钥给所有非被控节点
[root@ansible-server ~]# ssh-keygen
[root@ansible-server ~]# ssh-copy-id 192.168.159.131 #所有被控服务器
所有机器:
# systemctl stop firewalld
# systemctl disable firewalld
# setenforce 0
安装 ansible:
配置EPEL网络yum源
[root@ansible-server ~]# wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo https://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/epel-7.repo
安装:控制节点
[root@ansible-server ~]# yum -y install ansible
查看版本
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible --version
ansible 2.9.27
config file = /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
configured module search path = [u'/root/.ansible/plugins/modules', u'/usr/share/ansible/plugins/modules']
ansible python module location = /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/ansible
executable location = /usr/bin/ansible
python version = 2.7.5 (default, Oct 14 2020, 14:45:30) [GCC 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-44)]
5. 基本使用
语法:
# ansible <pattern> -m <module_name> -a <arguments>
pattern -- 主机清单里面定义的主机组名,主机名,IP,别名等,all 表示所有的主机,支持通配符,正则
: -- 多个组,组名之间用冒号隔开
"web" -- 组名或主机名中含有web的
webservers[0] -- webserver
以~开头,匹配正则
-m module_name: 模块名称,默认为command
-a arguments: 传递给模块的参数
最常用的模块:
command
shell
使用ping模块检查ansible节点的连通性:
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible ansible-web1 -m ping
ansible-web1 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible ansible-web1 -m ping -o
ansible-web1 | SUCCESS => {"ansible_facts": {"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"}, "changed": false, "ping": "pong"}
同时指定多台机器:
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible ansible-web1,ansible-web2 -m ping -o
ansible-web1 | SUCCESS => {"ansible_facts": {"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"}, "changed": false, "ping": "pong"}
ansible-web2 | SUCCESS => {"ansible_facts": {"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"}, "changed": false, "ping": "pong"}
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible ansible-web* -m ping -o
ansible-web2 | SUCCESS => {"ansible_facts": {"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"}, "changed": false, "ping": "pong"}
ansible-web1 | SUCCESS => {"ansible_facts": {"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"}, "changed": false, "ping": "pong"}
ansible-web5 | SUCCESS => {"ansible_facts": {"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"}, "changed": false, "ping": "pong"}
执行shell命令:
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible ansible-web1 -m shell -a 'uptime'
ansible-web1 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
12:18:53 up 4:49, 3 users, load average: 0.01, 0.03, 0.05
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible ansible-web1 -m command -a 'uptime'
ansible-web1 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
12:19:22 up 4:49, 3 users, load average: 0.00, 0.02, 0.05
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible ansible-web1 -a 'uptime'
ansible-web1 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
12:19:44 up 4:50, 3 users, load average: 0.00, 0.02, 0.05
使用ssh账号和密码:
- -u 用户 //指定ssh账户
- -k //指定使用ssh密码(注意:如果设置了公钥认证,这里写什么密码都可以)
注意:没有传公钥的其他账户就有用了,比如上面的root换成wing账户(前提:wing账户在被控制机器中已存在)
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible ansible-web1 -a 'uptime' -u root -k
SSH password:
ansible-web1 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
12:23:33 up 4:53, 3 users, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.05
给节点增加用户:
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible ansible-web1 -a 'useradd wing'
ansible-web1 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible ansible-web1 -a 'grep wing /etc/passwd'
ansible-web1 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
wing:x:1001:1001::/home/wing:/bin/bash
重定向输出到本地文件中:
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible ansible-web1 -a 'df -h' > /tmp/a.txt
[root@ansible-server ~]# cat /tmp/a.txt
ansible-web1 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
文件系统 容量 已用 可用 已用% 挂载点
devtmpfs 974M 0 974M 0% /dev
tmpfs 991M 0 991M 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 991M 11M 980M 2% /run
tmpfs 991M 0 991M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/mapper/centos-root 17G 5.4G 12G 32% /
/dev/sda1 1014M 173M 842M 18% /boot
tmpfs 199M 32K 199M 1% /run/user/0
/dev/sr0 4.4G 4.4G 0 100% /run/media/root/CentOS 7 x86_64
二:主机清单 inventory
inventory文件通常用于定义要管理主机及其认证信息,例如ssh登录用户名、密码以及key相关信息。
1. 配置文件
[root@ansible-server ~]# vim /etc/ansible/hosts
web1 #单独指定主机,可以使用主机名称或IP地址
web2
web3
#-------------------------------------------------------------
[webservers] #使用[]标签指定主机组
192.168.159.131
bar.example.com
up.example.com:5309 #指定 SSH 端口 5309
web5 ansible_ssh_host=web2 #设置主机web2的别名为 web5
web1 ansible_ssh_pass='123456' #设置ssh密码,使用-k参数之后提示的密码可以不写,直接回车
www[01:50].example.com #支持通配符匹配www01,www02,...,www50
db-[a:f].example.com #通配符匹配db-a,db-b,...,db-f
#-------------------------------------------------------------
# 为每个主机单独指定变量,这些变量随后可以在 playbooks 中使用:内置变量
[atlanta]
host1 http_port=80 maxRequestsPerChild=808
host2 http_port=303 maxRequestsPerChild=909
#-------------------------------------------------------------
#为一个组指定变量,组内每个主机都可以使用该变量
[atlanta]
host1
host2
[atlanta:vars]
ansible_ssh_pass='123456'
ntp_server=ntp.atlanta.example.com
proxy=proxy.atlanta.example.com
#-------------------------------------------------------------
#组可以包含其他组
[atlanta]
host1
host2
[raleigh]
host3
host4
[southeast:children] #southeast包括两个子组
atlanta
raleigh
[southeast:vars]
some_server=foo.southeast.example.com
halon_system_timeout=30
ansible基于ssh连接inventory中指定的远程主机时,还可以通过参数指定其交互方式。
ansible_ssh_host # 远程主机
ansible_ssh_port # 指定远程主机ssh端口
ansible_ssh_user # ssh连接远程主机的用户,默认root
ansible_ssh_pass # 连接远程主机使用的密码,在文件中明文,建议使用--ask-pass或者使用SSH keys
ansible_sudo_pass # sudo密码, 建议使用--ask-sudo-pass
ansible_connection # 指定连接类型: local, ssh, paramiko
ansible_ssh_private_key_file # ssh 连接使用的私钥
ansible_shell_type # 指定连接对端的shell类型, 默认sh,支持csh,fish
ansible_python_interpreter # 指定对端使用的python编译器的路径
2. 使用
查看组内主机列表
语法:ansible 组名 --list-hosts
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible raleigh --list-hosts
hosts (2):
host3
host4
自定义主机列表
[root@ansible-server ~]# mkdir /home/ansible
[root@ansible-server ~]# vim /home/ansible/hostlist
[all:vars]
ansible_ssh_port=22
ansible_ssh_user=root
ansible_ssh_pass=1
[all]
ansible-web1
ansible-web2
测试:
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible -i /home/ansible/hostlist all -m ping -o
ansible-web1 | SUCCESS => {"ansible_facts": {"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"}, "changed": false, "ping": "pong"}
ansible-web2 | SUCCESS => {"ansible_facts": {"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"}, "changed": false, "ping": "pong"}
注意:
一个典型的例子就是 shell 和 command 模块. 这两个模块在很多情况下都能完成同样的工作, 以下是两个模块之前的区别:
command 模块命令将不会使用 shell 执行. 因此, 像 $HOME 这样的变量是不可用的。还有像 |,& 都将不可用
shell 模块通过shell程序执行, 默认是/bin/sh, <, >, |, ;, & 可用
三:点对点 Ad-Hoc
ad hoc临时的,在ansible中是指需要快速执行,并且不需要保存的命令。其实就是执行简单的命令,对于复杂的命令则需要playbook。
1. ansible 模块
列出ansible支持的模块:
-l -- 获取列表
-s module_name -- 获取指定模块的使用信息
获取模块列表:
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible-doc -l
模块使用格式:
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible-doc yum
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible-doc -s yum
模块官方文档:https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/2.9/modules/list_of_files_modules.html
常用模块
用户管理模块:user
添加用户并设置密码:
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible ansible-web2 -m user -a "name=king password=`echo 1234 | openssl passwd -1 -stdin`" -o
ansible-web2 | CHANGED => {"ansible_facts": {"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"}, "changed": true, "comment": "", "create_home": true, "group": 1001, "home": "/home/king", "name": "king", "password": "NOT_LOGGING_PASSWORD", "shell": "/bin/bash", "state": "present", "system": false, "uid": 1001}
-1 MD5加密算法
删除用户:
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible ansible-web2 -m user -a "name=king state=absent" -o
ansible-web2 | CHANGED => {"ansible_facts": {"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"}, "changed": true, "force": false, "name": "king", "remove": false, "state": "absent"}
adsent #删除用户,但是不会删除家目录
组管理模块:group
添加组:
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible ansible-web2 -m group -a "name=ts state=present"
ansible-web2 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"gid": 1001,
"name": "ts",
"state": "present",
"system": false
}
删除组:
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible ansible-web2 -m group -a "name=ts state=absent"
ansible-web2 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"name": "ts",
"state": "absent"
}
软件包管理模块:yum
安装软件(apache):
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible ansible-web2 -m yum -a "name=httpd state=latest" -o
删除软件(apache):
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible ansible-web2 -m yum -a "name=httpd state=removed" -o
服务管理模块:service
案例:
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible ansible-web2 -m service -a "name=httpd state=started" # 启动
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible ansible-web2 -m service -a "name=httpd state=stopped" # 停止
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible ansible-web2 -m service -a "name=httpd state=restarted" # 重启
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible ansible-web2 -m service -a "name=httpd state=started enabled=yes" # 开机启动
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible ansible-web2 -m service -a "name=httpd state=started enabled=no" # 开机关闭
文件模块: file
参数:
owner:修改属主
group:修改属组
mode:修改权限
path=:要修改文件的路径
recurse:递归的设置文件的属性,只对目录有效
yes:表示使用递归设置
state:
touch:创建一个新的空文件
directory:当目录存在时不会进行修改
案例:
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible ansible-web2 -m file -a 'path=/tmp/b.txt mode=777 state=touch' //创建一个文件
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible ansible-web2 -m file -a 'path=/tmp/test mode=777 state=directory' //创建一个目录
收集信息模块:setup
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible ansible-web2 -m setup //收集所有信息
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible ansible-web2 -m setup -a 'filter=ansible_all_ipv4_addresses' //只查询ipv4的地址
查看主机内存信息
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible ansible-web2 -m setup -a 'filter=ansible_*_mb'
查看所有的网卡信息
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible ansible-web2 -m setup -a 'filter=ansible_ens*'
将所有主机的信息输入到/tmp/facts目录下:
每台主机的信息输入到主机名文件中(/etc/ansible/hosts里的主机名)
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible ansible-web2 -m setup --tree /tmp/facts
文件复制模块:copy
参数:
backup:在覆盖之前,将源文件备份,备份文件包含时间信息。有两个选项:yes|no
content:用于替代“src”,可以直接设定指定文件的值
dest:必选项。要将源文件复制到的远程主机的绝对路径,如果源文件是一个目录,那么该路径也必须是个目录
directory_mode:递归设定目录的权限,默认为系统默认权限
force:如果目标主机包含该文件,但内容不同,如果设置为yes,则强制覆盖,如果为no,默认为yes
others:所有的file模块里的选项都可以在这里使用
src:被复制到远程主机的本地文件,可以是绝对路径,也可以是相对路径。如果路径是一个目录,它将递归复制。在这种情况下,如果路径使用“/”来结尾,则只复制目录里的内容,如果没有使用“/”来结尾,则包含目录在内的整个内容全部复制
案例:
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible test -m copy -a "src=/srv/myfiles/foo.conf dest=/etc/foo.conf owner=foo group=foo mode=0644"
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible test -m copy -a "src=/mine/ntp.conf dest=/etc/ntp.conf owner=root group=root mode=644 backup=yes"
计划任务模块:cron
参数:
backup:对远程主机上的原任务计划内容修改之前做备份
cron_file:如果指定该选项,则用该文件替换远程主机上的cron.d目录下的用户的任务计划
day:日(1-31,*,*/2,……)
hour:小时(0-23,*,*/2,……)
minute:分钟(0-59,*,*/2,……)
month:月(1-12,*,*/2,……)
weekday:周(0-7,*,……)
job:要执行的任务,依赖于state=present
name:该任务的描述
special_time:指定什么时候执行,参数:reboot,yearly,annually,monthly,weekly,daily,hourly
state:确认该任务计划是创建还是删除
user:以哪个用户的身份执行
案例:
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible test -m cron -a 'name="a job for reboot" special_time=reboot job="/some/job.sh"'
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible test -m cron -a 'name="yum autoupdate" weekday="2" minute=0 hour=12 user="root
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible test -m cron -a 'backup="True" name="test" minute="0" hour="5,2" job="ls -alh > /dev/null"'
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansilbe test -m cron -a 'cron_file=ansible_yum-autoupdate state=absent'
2. 实战案例
获取每台主机的IP地址
获取每台主机的内存
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible ansible-web2 -m shell -a "free -m | awk 'NR==2'" > b.txt -o && cat b.txt | awk '{print $10}'
896
四:剧本 Playbook
1. 介绍
playbook是由一个或多个"play"组成的列表。play的主要功能在于将事先归为一组的主机装扮成事先通过ansible中的task定义好的角色。从根本上来将,所谓的task无非是调用ansible的一个module。将多个play组织在一个playbook中,即可以让他们联通起来按事先编排的机制同唱一台大戏。
playbook-->play-->task-->module
Playbook是Ansible的配置,部署,编排语言。他们可以被描述为一个需要希望远程主机执行命令的方案,或者一组IT程序运行的命令集合。当执行一些简单的改动时ansible命令是非常有用的,然而它真的作用在于它的脚本能力。当对一台机器做环境初始化的时候往往需要不止做一件事情,这时使用playbook会更加适合。通过playbook你可以一次在多台机器执行多个指令。通过这种预先设计的配置保持了机器的配置统一,并很简单的执行日常任务。
Playbook还开创了很多特性,它可以允许你传输某个命令的状态到后面的指令,如你可以从一台机器的文件中抓取内容并附为变量,然后在另一台机器中使用,这使得你可以实现一些复杂的部署机制,这是ansible命令无法实现的。
2. 格式
playbook由YMAL语言编写。YMAL格式是类似于JSON的文件格式,便于人理解和阅读,同时便于书写
3. 核心元素
- Variables // 变量元素,可传递给Tasks/Templates使用
- Tasks // 任务元素,由模块定义的操作的列表,即调用模块完成任务
- Templates // 模块元素,使用了模块语法的文本文件,可根据变量动态生成配置文件
- Handlers // 处理器元素,通常指在某事件满足时触发的操作
- Roles // 角色元素
注意:
一个剧本里面可以有多个play,每个play只能有一个tasks,每个tasks可以有多个name。
4. 基础组件
name:
定义playbook或者task的名称(描述信息),每一个play都可以完成一个任务。
hosts:
playbook中的每一个paly的目的都是为了让某个或某些以某个指定用户的身份执行任务;与命令模式下的ansible匹配规则一样。
user:
remote_user则用于指定远程主机上的执行任务的用户,也可以使用user(基本上是root)。
tasks:
任务列表play的主体部分是task list. task list中的各任务按次序逐个在hosts中指定的所有主机上执行。
vars:
定义变量(如果不使用内部变量需要提前定义)。
vars_files:
调用定义变量文件。
notify:
任务执行结果如果是发生更改了的则触发定义在handler的任务执行。
handlers:
用于当前关注的资源发生变化时采取一定指定的操作。
include:
能包含的包括task,handler和playbook;可以在include的时候传递变量。
五:剧本案例
1. 案例一
[root@ansible-server ~]# cd /etc/ansible/
[root@ansible-server ansible]# echo set nu ts=2 et cuc sw=2 autoindent > ~/.vimrc
[root@ansible-server ansible]# vim test.yml
1 ---
2 - hosts: ansible-web1
3 user: root
4 tasks:
5 - name: playbook_test
6 file: state=touch path=/tmp/playbook.txt
参数解释:
- hosts:参数指定了对哪些主机进行操作
- user:参数指定了使用什么用户登录远程主机操作
- tasks:指定了一个任务
- name:参数同样是对任务的描述,在执行过程中会打印出
检测语法:
[root@ansible-server ansible]# ansible-playbook --syntax-check test.yml
playbook: test.yml
运行playbook:
[root@ansible-server ansible]# ansible-playbook test.yml
PLAY [ansible-web1] ************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************
ok: [ansible-web1]
TASK [playbook_test] ***********************************************************
changed: [ansible-web1]
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************
ansible-web1 : ok=2 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
2. 案例二
handlers:由特定条件触发的 Tasks
语法:
# 调用及定义方式
tasks:
- name: TASK_NAME
module: arguments
notify: HANDLER_NAME
handlers:
- name: HANDLER_NAME
module: arguments
案例:
[root@ansible-server ansible]# vim handlers.yml
1 ---
2 - hosts: ansible-web1
3 user: root
4 tasks:
5 - name: test copy
6 copy: src=/root/a.txt dest=/mnt
7 notify: test handlers
8
9 handlers:
10 - name: test handlers
11 shell: echo "abcd" >> /mnt/a.txt
注意:
只有 copy 模块真正执行后,才会去调用下面的 handlers 相关的操作,追加内容。所以这种比较适合配置文件发生更改后,需要重启服务的操作。
检测语法:
[root@ansible-server ansible]# ansible-playbook --syntax-check handlers.yml
playbook: handlers.yml
运行剧本:
[root@ansible-server ansible]# ansible-playbook handlers.yml
PLAY [ansible-web1] ************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************
ok: [ansible-web1]
TASK [test copy] ***************************************************************
changed: [ansible-web1]
RUNNING HANDLER [test handlers] ************************************************
changed: [ansible-web1]
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************
ansible-web1 : ok=3 changed=2 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
[root@ansible-server ansible]# ansible ansible-web1 -m shell -a "cat /mnt/a.txt"
ansible-web1 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
ansible-web1 | UNREACHABLE!: Failed to connect to the host via ssh: ssh: connect to host ansible-web1 port 22: No route to host
abcd
3. 案例三
安装nginx并启动服务
[root@ansible-server ansible]# vim yum.yml
1 ---
2 - hosts: ansible-web1
3 user: root
4 tasks:
5 - name: install nginx
6 yum:
7 name: nginx
8 state: latest
9 notify: start nginx
10
11 handlers:
12 - name: start nginx
13 service:
14 name: nginx
15 state: started
检测语法:
[root@ansible-server ansible]# ansible-playbook --syntax-check yum.yml
playbook: yum.yml
运行剧本:
[root@ansible-server ansible]# ansible-playbook yum.yml
PLAY [ansible-web1] ************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************
ok: [ansible-web1]
TASK [install nginx] ***********************************************************
changed: [ansible-web1]
RUNNING HANDLER [start nginx] **************************************************
changed: [ansible-web1]
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************
ansible-web1 : ok=3 changed=2 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
[root@ansible-server ansible]# ansible ansible-web1 -m shell -a "systemctl status nginx"
ansible-web1 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
● nginx.service - nginx - high performance web server
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since 六 2025-03-08 17:43:37 CST; 11min ago
Docs: http://nginx.org/en/docs/
Process: 61202 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/nginx -c /etc/nginx/nginx.conf (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 61203 (nginx)
Tasks: 5
CGroup: /system.slice/nginx.service
├─61203 nginx: master process /usr/sbin/nginx -c /etc/nginx/nginx.con
├─61204 nginx: worker process
├─61205 nginx: worker process
├─61206 nginx: worker process
└─61207 nginx: worker process
3月 08 17:43:37 ansible-web1 systemd[1]: Starting nginx - high performance web server...
3月 08 17:43:37 ansible-web1 systemd[1]: Started nginx - high performance web server.
4. 案例四
循环:迭代,需要重复执行的任务
对迭代项的引用,固定变量名为 " item " ,使用 with_items 属性给定要迭代的元素
元素:1. 列表 2. 字符串 3. 字典
基于字符串列表元素实战
[root@ansible-server ansible]# vim list.yml
1 ---
2 - hosts: ansible-web1
3 user: root
4 tasks:
5 - name: install packages
6 yum:
7 name: "{{ item }}"
8 state: latest
9 with_items:
10 - httpd
11 - php
12 - php-mysql
13 - php-mbstring
14 - php-gd
检测语法:
[root@ansible-server ansible]# ansible-playbook --syntax-check list.yml
playbook: list.yml
运行剧本:
[root@ansible-server ansible]# ansible-playbook --syntax-check list.yml
playbook: list.yml
[root@ansible-server ansible]# ansible-playbook list.yml
PLAY [ansible-web1] ************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************
ok: [ansible-web1]
TASK [install packages] ********************************************************
[DEPRECATION WARNING]: Invoking "yum" only once while using a loop via
squash_actions is deprecated. Instead of using a loop to supply multiple items
and specifying `name: "{{ item }}"`, please use `name: ['httpd', 'php', 'php-
mysql', 'php-mbstring', 'php-gd']` and remove the loop. This feature will be
removed in version 2.11. Deprecation warnings can be disabled by setting
deprecation_warnings=False in ansible.cfg.
changed: [ansible-web1] => (item=[u'httpd', u'php', u'php-mysql', u'php-mbstring', u'php-gd'])
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************
ansible-web1 : ok=2 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
基于字典列表给元素实例
[root@ansible-server ansible]# vim zidian.yml
1 ---
2 - hosts: ansible-web2
3 user: root
4 tasks:
5 - name: create groups
6 group:
7 name: "{{ item }}"
8 state: present
9 with_items:
10 - groupx1
11 - groupx2
12 - groupx3
13
14 - name: create users
15 user:
16 name: "{{ item.name }}"
17 group: "{{ item.group }}"
18 state: present
19 with_items:
20 - {name: 'userx1',group: 'groupx1'}
21 - {name: 'userx2',group: 'groupx2'}
22 - {name: 'userx3',group: 'groupx3'}
语法检测:
[root@ansible-server ansible]# ansible-playbook --syntax-check zidian.yml
playbook: zidian.yml
运行剧本:
[root@ansible-server ansible]# ansible-playbook zidian.yml
PLAY [ansible-web2] ************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************
ok: [ansible-web2]
TASK [create groups] ***********************************************************
changed: [ansible-web2] => (item=groupx1)
changed: [ansible-web2] => (item=groupx2)
changed: [ansible-web2] => (item=groupx3)
TASK [create users] ************************************************************
changed: [ansible-web2] => (item={u'group': u'groupx1', u'name': u'userx1'})
changed: [ansible-web2] => (item={u'group': u'groupx2', u'name': u'userx2'})
changed: [ansible-web2] => (item={u'group': u'groupx3', u'name': u'userx3'})
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************
ansible-web2 : ok=3 changed=2 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
5. 案例五
tags使用
给指定的任务定义一个调用标识,形式如下:
只运行指定标记的任务:
[root@ansible-server ansible]# ansible-playbook -t mkdir tag.yml
跳过某一个被标记的任务:
[root@ansible-server ansible]# ansible-playbook --skip-tags=mkdir tag.yml
从某一个任务开始往下运行:
[root@ansible-server ansible]# ansible-playbook --start-at-task "mkdir file" tag.yml
案例
[root@ansible-server ansible]# vim tag.yml
1 ---
2 - hosts: ansible-web1
3 user: root
4 tasks:
5 - name: touch file
6 file: path=/root/11.txt state=touch
7 tags: touch_file1
8 - name: mkdir file
9 file: path=/root/mk state=directory
10 tags: mkdir
11 - name: touch file2
12 file: path=/root/22.txt state=touch
13 tags: touch_file2
检测语法:
[root@ansible-server ansible]# ansible-playbook --syntax-check tag.yml
playbook: tag.yml
6. 案例六
调用其他playbook
==> include.yml <==
1 ---
2 - import_playbook: test.yml
3 - import_playbook: tag.yml
==> test.yml <==
1 ---
2 - hosts: ansible-web2
3 user: root
4 tasks:
5 - name: playbook_test
6 file: state=touch path=/tmp/playbook.txt
==> tag.yml <==
1 ---
2 - hosts: ansible-web2
3 user: root
4 tasks:
5 - name: touch file
6 file: path=/root/11.txt state=touch
7 tags: touch_file1
8 - name: mkdir file
9 file: path=/root/mk state=directory
10 tags: mkdir
11 - name: touch file2
12 file: path=/root/22.txt state=touch
13 tags: touch_file2
检测语法:
[root@ansible-server ansible]# ansible-playbook --syntax-check include.yml
playbook: include.yml
运行剧本:
[root@ansible-server ansible]# ansible-playbook include.yml
7. 案例七
在 playbook 执行过程中暂停一定时间或者提示用户进行某些操作
常用参数:
- minutes:暂停多少分钟
- seconds:暂停多少秒
- prompt:打印一串信息提示用户操作
[root@ansible-server ansible]# vim wait.yml
1 ---
2 - name: wait
3 hosts: ansible-web1
4 tasks:
5 - name: wait on user input
6 pause: prompt="Warning! Detected slight issue. ENTER to co ntinue CTRL-C a to quit"
7 - name: timed wait
8 pause: seconds=30
检测语法:
[root@ansible-server ansible]# ansible-playbook --syntax-check wait.yml
playbook: wait.yml
运行剧本:
[root@ansible-server ansible]# ansible-playbook wait.yml
PLAY [wait] ********************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************
ok: [ansible-web1]
TASK [wait on user input] ******************************************************
[wait on user input]
Warning! Detected slight issue. ENTER to continue CTRL-C a to quit:
[[ok: [ansible-web1]
TASK [timed wait] **************************************************************
Pausing for 30 seconds
(ctrl+C then 'C' = continue early, ctrl+C then 'A' = abort)
ok: [ansible-web1]
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************
ansible-web1 : ok=3 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0